- Applications
- Bertrand Russell
- Autobiography (인생은 뜨겁게)
- Conquest of Happiness (행복의 정복)
- History of Western Philosophy - Bertrand Russell
- Marriage and Morality (결혼과 도덕)
- 11. 새로운 시대의 결혼법 (Trial Marriage or Companionate Marriage)
- 15. 행복한 이혼의 조건 (Divorce)
- 18. 사랑과 개인의 행복 (성교육) (Sex and Individual Well-Being)
- 19. 사랑과 인간의 가치 (Place of Sex Among Human Values)
- 20. Conclusion (자유로운 사랑과 행복한 결혼)
- 4. 사랑에 대한 기독교의 저주 (Christian Ethics)
- 5. 낭만적 사랑의 탄생 (Romantic Love)
- 6. 낭만적 사랑의 탄생 2
- 8. 사랑이 인생에 차지하는 위치 (The Place of Love in Human Life)
- 9. 결혼을 불행하게 만드는 것들
- Abelard and Heloise
- Jean Jacques Rousseau (루소와 낭만주의의 시작)
- 고금소총
- 박** 1
- 박** 2
- 일부일처제의 기원
- On Education (교육론)
- Selected Essays
- The Analysis of Mind (정신분석)
- The Praise of Idleness (게으름에 대한 찬양)
- The Problems of Philosophy (철학의 문제들)
- Why I am not a Christian (내가 왜 기독교인이 아닌 이유)
- 나는 무엇을 위해 살아왔는가?
- Biblical Studies
- General Questions
- Apostle Paul (사도바울의 사역)
- Bible Quiz and Jeopardy
- CM Bible Study
- David: A Man of Passion & Destiny - Charles Swindol
- Jesus and the Eyewitnesses - Richard Bauckham
- Jesus of Nazaret Short Clips
- A woman washes Jesus' feet with her tears
- Are you the Son of God, Jesus said I am
- Five Loaves and Two Fishes
- Jesus Baptized by John
- Jesus became angry at the temple
- Jesus enters into Jerusalem
- Jesus heals a sick man in bed
- Jesus Heals satan-possessed man
- Jesus heals the servant of a centurion
- Jesus Reads Scripture at Synagogue (안식일 회당에서 성경을 읽으신 예수님)
- Jesus said He will have a supper with Matthew
- Jesus' conversation with Pharasees about the greatest command
- Last Supper (최후의 만찬)
- Lazarus rise from death
- Love your enemy and new Jerusalem
- Miracle - Jesus heals a born-blind man
- Nicodemo and John 3-16
- Peter denies Jesus
- Sermon - be perfect, do not judge, seek
- Sermon - Do not worry about tomorrow
- Sermon - The Kingdom of heaven is like treasure hidden in the field
- Sermon on the mountain and Lord's Prayer
- The Story of Prodigal Son
- What authority and The story of two sons
- Woman of adultery (간음한 여인을 용서하시는 예수님)
- Kids Bible Study and Sermon
- Preaching Christ from the Old Testament by Sidney Greidanus
- Preaching from the Old Testament by Elizabeth Achtemeier
- Questions from my kids
- Anyone who does not know Jesus goes to hell. Isn't that unfare?
- Did Jesus feel pain on the cross? Why? He could have done something not to feel
- God promised a land. Buy why didn't most of Israel people get into that land?
- God used to speak to people long time ago, but not any more. Why?
- How to explain circumcision to my kids
- Is it Satan's fault or Adam's?
- Is Jesus the Son of God or God in human form?
- Was Peter Crucified Upside Down?
- Where Did Cain Get His Wife?
- Why did god plant the tree of knowledge of good and evil?
- Why did God strike Uzzah dead for touching the Ark of the Covenant?
- Why God Didn’t Make Man Perfect
- Why is the land of Canaan called "land flowing with milk and honey."
- Why is there so much evils in the world?
- Socratic Seminar for Bible Study
- Study with Worship Music
- The Parables of Jesus (예수님의 비유)
- The Westminster Shorter Catechism
- Youth Ministry Bible Study 2018 - 2019
- 3 Ways to Make Small Groups More Effective (AwanaYM)
- Anti-Intellectualism - The Great Awakening
- Apostles' Creed
- Arian Controversy
- Bible Study #11 - do all to the glory of God
- Bible Study #6 - Theology with worship music
- Bible Study #7 - The covenant of grace
- Bible Study #8 - Mosaic Covenant
- Bible Study #9 - New Covenant
- Covenant - What is it? Why is it important?
- Critcal Thinking about God - Anselm and Aquinas
- Discipleship, Is Jesus the only way?
- Esther 4 - If I parish I parish
- Esther 5 - Fictional elements in the story of Esther
- First Excuse of Human
- God of Love and God of Wrath
- Good college - good job - a lot of money?
- Idol Worship
- In an Age of Science, It’s Silly to Believe God Created Everything - Challenge Response
- Incarnation
- Martin Luther
- Psalm 22: ‘My God, My God, Why Have You Forsaken Me?’
- Psalm: 104:5 - The earth as the center of the world
- Puritanism
- Romans 10
- St. Anselm's Ontological Argument
- The Beatitudes (Matthew 5)
- The burden of sin, The slave of sin, The power of sin
- The Case for Christ
- The difference between religion and the gospel
- The History of Worship Music in the Church
- The Parable of the sower - 씨뿌리는 자의 비유 (마태복음 13장)
- The Problem of Evil
- The Problem of Evil (Powerful God, then why?)
- The Scripture - view as mirror or window?
- The Translation of the Bible
- The Westminster Shorter Catechism
- Three ways to know God (성경, 이성, 경험)
- Utilitarianism
- What's so amazing about grace?
- Who is C.S. Lewis?
- Why are so many young people leaving the chuch?
- Why Can't More Christians Perform Miracles?
- Why doesn`t the book of Esther mention God?
- Youth Ministry Small Group Questions (AwanaYM)
- 군대이야기, 어릴적 비디오게임
- Youth Ministry Bible Study 2019 - 2020
- 구약성경
- 성서 비평학(Higher Criticism)
- 예수님의 비유 - 최갑종
- 1. 비유와 그 해석
- 10. 달란트 비유
- 11. 불의한 청지기 비유 (The Parable of the Dishonest Manager)
- 2. 장터에서 노는 아이들의 비유 (마 11:16~18, 눅 7:31~35)
- 3. 씨뿌리는 자의 비유 (마 13:1~9, 막 4:1~9, 눅 8:4~8)
- 4. 겨자씨의 비유 (마 13:31~32, 막 4:30~32, 눅 13:18~19)
- 5. 가라지 비유 (마 13:24, 36~43)
- 6. 선한 사마리아 사람의 비유 (눅 10:25 ~ 37)
- 7. 용서하지 않은 종의 비유
- 8. 포도원 품꾼의 비유
- 9. 아버지와 두 아들이 비유
- Biographies
- Business and Leadership
- Courageous Leadership - Bill Hybels
- Fight Mediocrity - Animated Book Reviews
- Great Speeches
- Abraham Lincoln - The Gettysburg Address(1863)
- Bill and Melinda Gates' 2014 Stanford Commencement Address
- Bill Gates Harvard Commencement Address 2007
- Einstein - Menace of Mass Destruction Speech
- Facebook COO Sheryl Sandberg Commencement Speech | Harvard Commencement 2014
- Martin Luther King Jr. - The March on Washington Address
- Oprah Winfrey Harvard Commencement speech | Harvard Commencement 2013
- President John F. Kennedy's Inaugural Address
- Steve Jobs' 2005 Stanford Commencement Address
- How to Win Friends and Influence People
- Investopedia
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
- Balance Sheet
- Compound Interest
- Cost Basis Basics
- Hedge Funds
- Interest Rates (Nominal and Real)
- Investment Real Estate
- Mutual Funds
- Nash Equilibrium
- Return On Investment (ROI)
- Time Value Of Money
- Understanding Profit Margin
- What are stocks?
- What Is Inflation?
- What is Trust Fund
- Working Capital
- John Maxwell Maximum Impact Club
- Becoming a leader-communicator
- Growing yourself, Growing others, Growing together
- Important Phrases at an important phase in my life
- Leading where no one has gone before
- Lets talk about books
- Lifting People to a higher level
- Making good decisions better
- Picking Potential Leaders
- Six Temptations
- The 5 Levels of Leadership - animated book summary
- The test of timing
- Things that do not require Talent
- Whatever it takes
- Words to live by
- Leadership and Business
- I Can't Accept Not Trying - Michael Jordan
- Built to last
- Byron Wien - Lessons Learned in His First 80 Years
- Developing the leader within you (John C. Maxwell)
- Fred Factor (Mark Sanborn)
- See you at the top (Zig Ziglar)
- The 17 Indisputable Laws of Teamwork
- The 21 Irrefutable Laws of Leadership (John C. Maxwell)
- 마케팅 불변의 법칙
- Ministry Toolbox
- Power your tribe - Christine Comaford
- Rich Dad Poor Dad
- Successful Business Men
- The Presentation Secrets of Steve Jobs - Carmine Gallo
- The Snowball: Warren Buffett and the Business of Life
- 지적대화를 위한 넓고 얕은 지식 - 채사장
- C.S. Lewis
- Collection of Good Analogies
- Collection of Good Questions
- Collection of Short Essay
- Introduction to Athanasius' On The Incarnation
- Learning in War-Time (English version)
- Learning in War-Time (전시의 학문)
- Modern Theology and Biblical Criticism - from Christian Reflection
- Reflection on The Psalms (시편묵상)
- The Problem of Pain (고통의 문제)
- The Seeing Eye
- The Weight of Glory (영광의 무게)
- Was C.S. Lewis A Calvinist?
- Why I'm Not a Pacifist
- Mere Christianity
- Collection of Good Analogies
- Chess and Go
- Chess Openings
- Chess Strategy and Puzzle
- Casino Royal Poker Scenes
- Chess Basics: Opening Principles
- Chess Openings- Halloween Gambit
- Chess Openings- The King's Gambit
- Chess Openings: Danish Gambit - Attacking Strategy
- Chess Openings: Giuoco Piano
- Chess Openings: Ruy Lopez
- Chess Openings: Sicilian Defense
- Chess Openings: The Queen's Gambit
- Chess Strategies- Skewers and Pins
- Chess Strategy- Trading Part 2
- Chess Traps: Bobby Fischer Trap
- Famous Chess Game: Kasparov vs Topalov 1999
- How to play poker
- Learn Chess: How to Castle
- Midland Xtra Talk
- Puzzle Solution - MonkeyPodGames.com
- Rubik's Cube
- Rubik's Cube 4x4
- Sicilian Defense - Najdorf Variation
- chess.com Lessons
- chess.com Video Lessons
- Basic Strategy
- Every Chess Opening: The First Move!
- Everything You Need to Know 2: The Opening!
- Opening - How to Crush Your Opponent With The King's Gambit -- Part 1
- Opening - How to Crush Your Opponent With The King's Gambit -- Part 2
- Opening - Ruy Lopez: The Verdict On 4.Nge7 (Advanced)
- Tactic - Patterns Everyone Must Know: Basic Tactics - 1!
- Tactic - Patterns Everyone Must Know: Basic Tactics - 2!
- Tactic - Patterns Everyone Must Know: Beyond the Basics 1!
- www.cyberoro.com
- 넷마블 바둑 강좌
- Go for Beginners: Short 9x9 Game Walkthroughs vs. igowin (Session #1)
- 넷마블 바둑 강좌 - 기초강좌 (1), 소목정석, 수상전
- 넷마블 바둑 강좌 - 기초강좌 (10), 포석, 사활 (환격, 5궁도, 후절사)
- 넷마블 바둑 강좌 - 기초강좌 (16), 기초사활
- 넷마블 바둑 강좌 - 기초강좌 (18, 19), 실전포석이론, 행마의 기초
- 넷마블 바둑 강좌 - 기초강좌 (19) : 행마의 기초
- 넷마블 바둑 강좌 - 기초강좌 (20, 21), 양단수, 요석과 페석
- 넷마블 바둑 강좌 - 기초강좌 (5), 장문, 촉촉수, 행마의모양, 화점정석
- 바둑 관련 서적
- 바둑격언모음
- 바둑용어
- 온라인 바둑 (Online Go)
- 정석 - 붙여막기 정석 (이창호정석)
- 정석 - 화점정석
- 바둑 초보자가 알아야 할 100가지
- 바둑강좌
- 바둑기보 모음
- Christian Apologetics
- Alvin Plantinga
- Cults
- A History of Defending The Truth: Heresy ? Alister McGrath
- A Topical Study of the Qur'an
- Are Mormons Closer to Muslims or Christians?
- Heretics Abound! Marcion, Montanus and Mormonism
- Islam - The Prophet and the Messiah - An Arab Christian's Perspective on Islam & Christianity
- Jehovah's Witness and Mormonism Comparison
- Similarities between Mormonism and Islam and differences
- Video website from Mormon
- Debate
- Evolution and Creationism
- Intelligent Design
- Jehovah's Witnesses
- Charles Taze Russell
- Debate: Is the Trinity Doctrine Biblical?
- Jehovah's Witnesses and the Trinity: A Christian Perspective
- Questions to Ask
- Trinity - Sources Misquoted (from jwfacts.com)
- Why the Jehovah's Witnesses don't want you to know about their founder: Charles Taze Russell
- Witnessing to the Witnesses - Understanding and Responding to False Doctrine
- 삼위일체를 부정하는 여호와의 증인들
- 삼위일체에관한 성경적 근거
- 성경신학과 조직신학의 차이점 (The Difference between Biblical Theology and Systematic Theology)
- 세르베투스(Michael Servetus) - 삼위일체를 반대한 중세 학자
- 아리우스주의(아리아니즘, Arianism)
- 여호와(Jehovah) 그 이름이 생겨난 배경
- 여호와의 증인관련 Resource Sites
- 여호와의 증인들과의 대화에서 느낀점들
- 여호와의 증인이 말하는 삼위일체 (1)
- 최삼경 목사의 여호와의증인 비판1: 자가당착식 삼위일체관
- 최삼경 목사의 여호와의증인 비판2: 편의주의적 성경관
- Kingdom of Cults - Walter Martin
- Lee Strobel
- Love Your God With All Your Mind - J. P. Moreland
- Mormon
- Question and Answer
- Didn't the idea of Jesus as divine Son of God only develop many years later after his death? (전설? 신화?)
- Errors in the Bible and Mythical Elements
- God as a means to an end - 갑자기 안하던 새벽기도를 나가는 이유?
- How can Jesus forgive a sin that is done againt someone else, not Jesus.
- Natural selection, Survival of the fittest, what is wrong with that (양육강식 무엇이 문제인가?)
- Partial Acceptance of the Bible 성경의 어떤 부분은 받아들이지만 어떤 부분은 받아들이기 힘들다
- Strong Rationalism. 난 이성적으로 납득이 안되는 것들은 받아들일수 없다
- What good can come out from Christianity (Nazareth) ?
- What if Jesus truly believed he was God when he is not actually? (완벽한 사기?)
- What is Scientific Proof? 우리가 과학적 증명이라고 말하는 것은 무엇인가?
- Which Christianity? 기독교를 반대한다면 도대체 어떤 기독교를 반대하는가?
- Why did God strike Uzzah dead for touching the Ark of the Covenant?
- Why did Jesus become human? (왜 인간으로 오셔야만 했나?)
- Why does not God clean up all evils? (왜 세상에 죄악이 가득하게 놔두시나?)
- Why is God so angry in the Old Testament and so loving in the New?
- Will Those Who Have Never Heard the Gospel Be Lost?
- Short Apologetics for Kids
- Stand To Reason
- Theological Differences
- Veritas Forum
- Alvin Plantinga - The Existence of Evil and the Problem of God
- Dallas Willard - Nietzsche vs. Jesus Christ: Who holds the true path?
- John Lennox - Christianity and the Tooth Faith
- John Lennox - Miracles: Is Belief in the Supernatural Irrational?
- Peter Kreeft - The Problem of Evil and Suffering: How could God allow it?
- Timothy Keller - Exclusive Religion in a Pluralistic Society
- William Lane Craig - 7 Reasons God Exists and Why it Matters
- When Skeptics Ask - Norman Geisler, Ron Brooks
- Christian Classics
- Church History
- Early Middle Ages - Paul Feedman at Yale University
- 1. Rome's Greatness and First Crises
- 10. Clovis and the Franks
- 11. Frankish Society
- 12. Britian and Ireland
- 13. Monasticism
- 14. Mohammed and the Arab Conquests
- 15. Islam Conquests and Civil War
- 16. The Splendor of the Abbasid Period
- 17. The Crucial Seventh Century
- 18. The Splender of Byzantium
- 19. Charlemagne
- 2. The Crisis of the Third Century and the Diocletianic Reforms
- 20. Intellectuals and the Court of Charlemagne
- 21. Crisis of the Carolingians
- 22. Vikings / The European Prospect, 1000
- 3. Constantine and the Early Church
- 4. The Christian Roman Empire
- 5. St. Augustine's Confession
- 6. Transformation of Roman Empire
- 7. Barbarian Kingdoms
- 8. Survival in the East
- 9. The Reign of Justinian
- Aristotle's Children - Richard Rubenstein
- Bernard of Clairvaux
- Chapter 1 -
- Chapter 2 -
- Chapter 3 - His Books Have Wings
- Chapter 4 - Aristotle among the heretics
- Chapter 5 - Aristotle and the teaching friars
- Chapter 6 - Thomas Aquinas
- Chapter 7 - William Ockham
- Chapter 8 - Aristotle and the modern world
- John Duns Scotus
- Meister Eckhart
- Peter Aberald
- Pope Boniface VIII
- Richard Rubenstein
- Who Were the Borgias?
- William of Ockham
- Christian History Made Easy
- Chapter 1 - The Gospel, the Apostle, then what? (AD 64 - 177)
- Chapter 10 - You Say You Want a Revolution? (AD 1620 - 1814)
- Chapter 11 - Optimism Has Its Limits (AD 1780 - 1914)
- Chapter 12 - Modern, Postmodern and Beyond (1906 - 2009)
- Chapter 2 - Balancing the Past and the Present (AD 90 - 250)
- Chapter 3 - The Church Wins and Loses (AD 247 - AD 420)
- Chapter 4 - Servant-Leaders or Leaders of Servants (AD 376 - 664)
- Chapter 5 - From Multiplication to Division (AD 496 - 1291)
- Chapter 6 - God Never Stops Working (673 - 1295)
- Chapter 7 - Everything Falls Apart (1294 - 1517)
- Chapter 8 - Wild Pigs in a Dirty Vineyard (AD 1500 - 1609)
- Chapter 9 - Change Doesn't Always Do You Good (AD 1510 - 1767)
- Why does church history matter?
- Church History
- 100 Most Important Events in Church History
- AD70: Titus destroys Jerusalem
- Athanasius: Meditations on the Incarnation
- Athanasius: on the incarnation - Summary
- Augtsine: book review The City of God by George Grant
- Augustine: on the Trinity - review from Theology for the Masses
- Christ and Culture, by the American theologian H. Richard Niehbuhr
- Dark Ages
- Early Christian Schisms - Ephesus, the Robber Council, and Chalcedon - Extra History - #4
- He Descended Into Hell?
- The Book That Changed the World (King James Bible)
- The Council of Nicaea (AD 325)
- The Great Revolt of Jews against Roman Rules
- The New Concise History of Crusade
- The Rise and Fall of Islamic Spain
- The second and the third Crusade
- Thirty Years' War
- Why Do People Hate The Jews?
- Church History from Worldwide Classroom
- Lesson 1 - The Study of Church History
- Lesson 10 - The Beginning of Monasticism
- Lesson 11 - Donatism
- Lesson 12 - The Council of Nicea
- Lesson 13 - Cappadocians and Constantinople
- Lesson 14 - Ambrose, Jerome and Chrysostom
- Lesson 15 - Augustine's Confession
- Lesson 16 - Augustine and the Pelagian Controversy
- Lesson 17 - Augustine's Theology of History
- Lesson 18 - The Council of Chalcedon
- Lesson 19 - The Early Middle Ages
- Lesson 2 - The Growth of the Christian Church
- Lesson 20 - Medieval Missions
- Lesson 21 - The Christianization of Great Britain
- Lesson 22 - Learning and Theology
- Lesson 23 - Eastern Orthodoxy
- Lesson 24 - The Late Middle Ages
- Lesson 25 - Medieval Monasticism
- Lesson 26 - Crusades or Missions
- Lesson 27 - The Waldensians
- Lesson 28 - Scholastic Theology
- Lesson 29 - Thomas Aquinas
- Lesson 3 - The Persecutions
- Lesson 30 - The Sacramental System
- Lesson 4 - The Apologists
- Lesson 5- Orthodoxy and Heresy
- Lesson 6 - Canon, Creed and Bishops
- Lesson 7 - The Early Church Fathers
- Lesson 8 - The People of the Early Church
- Lesson 9 - The Church in the Fourth Century
- Church History Magazine
- Church History, Volume Two: From Pre-Reformation to the Present Day
- Historical Theology by Ryan Reeves - Gorden Conwell
- History of Christianity in America and Canada
- Meister Eckhart - German Mysticism
- When Jesus Became God - Richard Rubinstein
- Early Middle Ages - Paul Feedman at Yale University
- Collection of Old Documents
- 60 Minutes Interview and More People
- Art Images and Paintings
- Biblical Study
- Biographies
- Chinese Calligraphy Tutorial
- Dance
- EBS Language (영어회화, 문법)
- Farming and Garden
- All kinds of Vegitables
- Azalea - Kurume, Satsuki, Encore
- Azalea (연산홍) - Satsuki, Kurumi Bonzai
- Belgium Giant Tomatoes
- Common Raised Garden Bed Mistakes (To Avoid)
- Coral Bells Azalea - 우리집꽃
- Dahlias - 우리집 꽃
- Fertilizer Basics
- Grape Arbor
- Heirloom Tomatos
- How to grow Heirloom Tomato for size
- How to prune grapes
- Hydrangea - 우리집 꽃
- New Flowers (2025)
- What is Loam soil?
- Zucchini Squash
- 고구마 키우는 방법
- 대봉감, 홍시
- 배나무 키우기
- 배추심는 시기 (무우)
- 사과나무 키우기
- 수박 키우기
- 애호박 키우기
- 오이키우기
- 우리집 Azaleas
- 우리집 flowers
- 참외 순따주기
- 포도나무 키우기기
- Fresh Air - Terry Gross
- Golf Lessons
- Golf Rule
- Golf Swing
- 리디아 고
- 신나송 - Golf Buddy
- (최대룡프로) 손목로테이션, 드라이버,
- [MY고덕호초청필드레슨]비거리 늘려준 스윙 - 맹동섭프로 초청 2편
- [골프레슨] 클럽 헤드를 던지는 방법! (hand rotation)
- [골프맨] 드라이버, 히터가 아닌 스윙어가 되자
- AC Separation
- Ben Hogan - The Five Lessons (Fundamentals)
- GolfDigestTV
- Me & My Golf Swing - Lag drill to crush your irons
- MySwingEvolution - Ben Hogan Basics: The Release
- Perfect Driver Takeaway
- Power Load Drill (함석철 리스트)
- Putting Basics
- Putting Tip - World's Best 3 Putting Drills
- Rory McIlroy 2013 LONG IRON with practice golf swing
- Roy Mcllroy Driver and Iron Swing (bauercti)
- Scratch Golf Academy - Iron
- Squatting! to increase distance and accuracy_JimMclean golf school
- Supination! To make the Hand first and Downblow shot
- Tiger Woods
- Tips to remember
- Top Speed Golf - Dibot after hitting the ball, Weight shift
- 공이 발보다 낮거나 높거나
- 김규동 - 팔로우 스루의 이해
- 김민휘의 드라이버 샷의 고정관념을 깨자 (Driver Slow motion)
- 김효주 - 2013 Driver vs Wedge Dual View golf swing
- 김효주 - 스윙기본 (Take away and Lead by hand)
- 김효주 스윙의 생명은 척추 각도 유지 & 스윙리듬
- 김효주 프로가 알려주는 비거리도 늘리고 방향성
- 무릎의 길은 기차길, 오른쪽 힙에서 체중이동
- 볼과 몸 사이의 올바른 간격
- 샬로윙의 원리와 방법 | 다운스윙 궤도
- 아이언 눌러치는 방법
- 오른발이 바깥쪽으로 도는 경우
- 이범주 - Inside Impact 안시현의 강한 임팩트 만들기
- 임연석 프로의 왼발이 낮거나 높은 경사지 상황
- 잘못된 골프백스윙궤도의 유형과 교정방법
- 전인지의 드라이버 연속 스윙
- 체중이동연습
- 치킨윙을 고치는 방법
- 칩샷, 이렇게만 하면 OK [MY고덕호필드레슨]
- 프로 스킬 배우기 - 스핀샷 - 권명호
- 핀까지 80미터, 버디할 수 있을까? [MY고덕호필드레슨]
- 헤드 스피드를 늘리고 싶다면 꼭 봐야 할 레슨! (권민경 프로)
- How to Ski
- Injury Related Information
- AC Separation
- Calf Muscle Tear (종아리근육 파열)
- How to Digest Protein: Your Health Depends on It
- Scoliosis
- Scoliosis - Asynchronous neuro-osseous growth in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
- Scoliosis - Uncoupled Neuro-Osseous (Chinese research in 2010)
- Scoliosis related terms
- 부부 관계를 안하면 남자와 여자, 누구에게 손해일까?
- 축구관련 음식과 영양 (구본준스포츠 재활센터)
- 탄수화물의 체내역할
- 허벅지 앞근육 타박상 (구본준스포츠 재활센터)
- Learning Japanese
- Ministry
- Miscellaneous
- Audible Book List
- edging
- Life Insurance Policy (생명보험 계약서)
- old pictures
- Picnic Game Ideas
- Pinewood School Report
- Scavenger hunt for Christian birthday party Feb-11-2018
- The Everest Avalanche, 18 April 2014, an eyewitness film
- What's the difference with HDMi 2.0 vs 2.0a?
- why do some people turn to homosexual
- 경희대학교 도서관
- 장수황씨 - 통일신라말기 황경의 후예들, 황희정승
- 차영석 결혼식
- Music
- Philip Yancey
- Poems
- I apologize - Emma
- Maybe
- 가난한 새의 기도 - 이해인
- 가시나무 - 하덕규
- 가을의 기도 - 김현승
- 가지 못한 길 - 로버트 프로스트
- 감사하다 - 정호승
- 고정희 - 사랑법 첫째
- 그대가 곁에있어도 나는 그대가그립다 - 류시화
- 그대를 사랑하는 - 서정윤
- 그런 사람이었으면 좋겠다 -
- 기쁜 우리 젊은 날 (이문열)
- 김광규 조개의 깊이
- 깃발 - 유치환
- 꽃 - 김춘수
- 낙화(落花) - 이형기
- 내가 사랑하는 사람 - 정호승
- 너에게 띄우는 글 - 이해인
- 눈물 - 서정윤
- 님의 침묵(沈默) - 한용운
- 모래위의 발자국 - 작자 미상
- 목마와 숙녀 - 박인환
- 못잊어 - 김소월
- 박정대 - 사랑과 열병의 화학적 근원
- 복종 - 한용운
- 사랑그대로의 사랑 - 유영석
- 사랑을 비웃는 사람들 - 김한길
- 사랑을 위한 충고 - 신진식
- 사랑의 메시지 - 고운
- 사모 - 조지훈
- 서시 - 김남조
- 서시 - 윤동주
- 옛 노트에서 - 장석남
- 윤동주 - 병원
- 이름없는 여인이 되어 - 노천명
- 진달래꽃 - 김소월
- 진은영 - 나는 오래된 거리처럼 너를 생각하고
- 푸르른 날 - 서정주
- 행복 - 유치환
- 홀로서기 - 서정윤
- Sermons and Columns
- Sjsoccer.org
- AAA Home owner's insurance and Auto
- Apple Care
- AT&T
- Cal Water
- charles schwab
- Chase J.P. Morgan
- citi bank
- COBRA Health Insurance
- DMV
- Fastrack
- Garbage
- Kaiser Health Plan
- Life Insurance Protective Life
- Living Trust
- Messi/Alves warm-up
- PG&E
- Property Tax
- State Farm auto insurance
- Tax Report
- TheTollRoads.com
- wells fargo
- www.jongha.com
- www.sjsoccer.org
- Xfinity
- 하나은행
- Soccer Drills (축구)
- Barcelona Stealing Game
- Calf Workout
- Cristiano Ronaldo & Gareth Bale Longshot Knuckleball Tutorial
- Crossing and Overlapping in the Diamond
- Insane FIFA 15 Skill Moves
- Passing in Square
- Soccer Moves To Beat A Defender
- Speed for Soccer with Speed Ladder and Cone bar
- Speed Hurdle
- Speed Ladder
- Sprint Drills for Speed
- Training for Speed
- Youbtube Channel - SoccerCoaches
- 롱킥하는 방법
- Soccer Videos
- 5 Times Lionel Messi Silenced Santiago Bernabeu
- Argentina vs. Netherlands WC 2014 Semifinal Highlights
- Barcelona Short Game Practice
- Barcelona vs Real Madrid 38-20 All Goals in La Liga 2008-2016
- Cristiano Ronaldo - Destroying Premier League - 2003-2009
- Cristiano Ronaldo - Dribbling Skills 2015
- Cristiano Ronaldo 2013-2014
- Cristiano Ronaldo Amazing Freestyle
- England Team - Attack
- England Team - Freekick
- England Team - Touch and Shoot
- FC Barcelona - This Is Football - HD
- FC Barcelona vs Arsenal 17-8 All Goals
- Kaká ● The Ultimate Show ● 2001-2013
- Lewandiwski
- Lionel Messi - 10 Magisterial Dribble-Goals
- Lionel Messi - A God Amongst Men HD
- Lionel Messi - Crazy Dribbling Skills - 2015 HD
- Lionel Messi - Simply Inexplicable
- Lionel Messi - The Greatest Ever - The Movie - HD
- Lionel Messi - Top 50 Goals - 2004-2013
- Lionel Messi vs Eibar ULTRA 4K (Home) 19/09/2017 by SH10
- Lionel Messi Vs Manchester United (2009)
- Lionel Messi vs Manchester United (Away) (2007-08)
- Messi vs Neymar
- Neymar - Amazing Skills 2013-2014
- Neymar - Ultimate Skills For Brazil 2010 - 2015
- Neymar vs Villarreal ULTRA 4K (Home) 06/05/2017 by SH10
- Real Madrid vs Barcelona 2-3 - UHD 4k La Liga 2016/2017 - Full Highlights
- Real Madrid vs Juventus 2018 Champions League Final 4K
- Ronaldinho - Freestyle
- Ronaldinho - Impossible to Forget
- Swimming
- Breaststroke - Sports and Outdoor
- Breaststroke from Speedo
- Breaststroke Kick Drills
- Butterfly - Michael Phelps Wins Gold - Men's 100m
- Butterfly - Speedo
- Common Freestyle Mistakes in Swimming
- Diving Progression for Swimming
- Freestyle Swimming - Speedo
- Freestyle Swimming Drills: Fingertip Drag
- Freestyle Swimming Drills: Flip-turn Progression
- How to Dive for Swimming
- How to Flutter Kick when Swimming Freestyle
- How to Side-breathe when Swimming Freestyle
- How to Swim Bent-arm Freestyle
- Intro to Swimming Freestyle
- Travel Guide
- Adjusting Guitar Truss Rods
- Aspen Colorado
- Banff
- Carmel Restaurants
- Hawaii - Ohau
- Kyoto Japan
- Napa Valley Restaurants
- office desk
- Oregon for summer mountains
- Paris - things to do
- Paris, 지명 pronouciation
- Quebec, Canada
- Ski at Switzerland (Saas-Fee Glacier)
- Switzerland
- Top-ten in Las Vegas
- Top-Ten Places to Visit in Canada
- Vancouver Canada, Baff, Lake Luise
- Wineries in Napa Valley
- 불어회화
- 유명한 식당
- 파리 여행 가이드 했던 분 (게으른 완벽주의자)
- 파리 외관 유명한데
- 파리여행 준비물
- 프랑스 식당 메뉴
- Writings for Young Adults
- 전병욱목사 칼럼모음
- 마취과 의사와의 만남
- 그리스도인의 사치-(2000/8/22)
- 눈썰매 타는 목사
- 독서와 그리스도인-(2000/8/8)
- 목사와 눈물-(2000/10/10)
- 미인의 기준이 바뀌어야 한다 (7/15/01)
- 새벽 문화를 만드는 전략 (8/5/01)
- 성도는 보수를 지지해야하나, 진보를 지지해야하나? (8/26/01)
- 시간을 구속하라-(2001/8/1)
- 시카고 대학에서 느낀 단상들
- 여성들이여 분발하라-(2000/8/15)
- 연상의 여인과 결혼하는 남자가 늘어나는 이유
- 영적 프론티어-(2000/9/26)
- 예수님의 웃음-(2000/10/3)
- 왜 늙은 남자는 젊은 여자를 좋아하나?
- 인정해 줄 때와 사랑해 줄 때-(2000/9/12)
- 일본에 부흥이 일어나지 않는 이유
- 지각은 범죄이다!
- 지도자의 자기통제-(2000/9/19)
- 차림새와 마음가짐-(2000/10/17)
- 청빈(淸貧)사상과 청부(淸富)사상
- 클린트 이스트우드를 바라보며
- 편작의 비밀
- 피터 드러커에게 배우라
- 효과적인 단기선교의 4가지 단계-(200/8/29)
- Computer Programming
- Actionscript
- Actionscript Dictionary
- Actionscript for Multiplayer Games and Virtual Worlds. - Jobe Makar
- Avoid ints in ActionScript
- blogs
- Colin MookPresentation Lesson
- Design Pattern : Template Pattern
- Event propagation or Event flow
- Glossary
- How to
- Object-oriented programming concepts: Inheritance (overriding)
- Object-oriented programming concepts: Polymorphism and interfaces
- Procedural Versus Object-Oriented
- Quick questions and answers
- Shadowbox and JW FLV media player
- Ajax
- About JSMX
- Ajax Document Management System
- Ajax Pattern
- Ajaxian Blog for all kinds of technologies
- ASP.NET AJAX toolkit
- Coldfusion Ajax Frameworks
- google web tool kit
- google-suggest like display
- iframe example from deveoper.apple.com
- Infragistic NetAdvantage : Ajax and ASP.NET
- Sending Data with Spry
- Spry Example: Check if user exists
- Submitting forms using AJAX
- updating back-end data with Spry
- Apache
- CodeIgniter
- ColdFusion
- Adobe ColdFusion Builder CFC Generator
- Ben Forta
- Blog and Resources
- ColdFusion related blog
- Converting Database queries to XML
- Creating A Remember Me Login System In ColdFusion
- Doing a form POST in Spry
- Form Post in Spry
- How to connect ColdFusion and MySQL
- How to use soEditor with ColdFusion on Linux
- Object Oriented ColdFusion
- Raymond Camden ColdFusion Blog
- Sending Data with Spry
- CSS
- 57+ Free Image Gallery, Slideshow And Lightbox Solutions
- blog design and layut
- Bootstrap
- Bootstrap for iPhone or iPad
- Bootstrap Tutorial Videos
- CKEditor - add bootstrap style in toolbar
- CKEditor Customization
- Clearfix CSS Hack
- Creating the Navigation Selector
- CSS example Eric CSS
- CSS example Zengarden
- Eric Myer on CSS
- Font on the web you can download
- Free Website Template - Hair Salon
- Front-end framework or template
- Frontend framework related slides from slideshare
- Good Design Websites and Online Resources
- How to make favicon and apple touch icon
- Icon collection
- Listicmatic style (list related stylesheet) max design
- QuirksMode.org by Peter-Paul Koch
- The dynamic stylesheet language
- Themes and wordpress elegant theme
- Writing CSS with LESS
- Design Pattern
- Final Cut Pro
- Flash
- Flex
- 15 Creating Skins and Themes in Flex
- A Better Model Object
- Array vs. ArrayCollection in Flex 2 (with a ColdFusion Slant)
- Blog Collection
- ColdFusion and Flex: Do you need Flex Data Services?
- context root has not been defined
- Cool Flex Application List
- Firefox Tip - Opening Flex Apps In The Current Tab
- Flex Articles
- Flex Builder 3 and Java Development Tool
- Flex Builder Tips
- Flex Cairngorm based contact manager
- Flex Data Service Tutorial
- Flex RemoteObject
- Flex Resource and Reference
- Flex Theme list
- Flex User Group
- How to dispatch an event from a custom item renderer
- How to install latest Flex SDK on Flex Builder
- Importing Flash CS3 Assets into Flex
- Integrating Flex 2 with ColdFusion MX
- Mixing HTML and Flex using IFrame
- Moving data from ColdFusion CFCs to Flex 2
- Sample Application and Code
- Terms and definition
- Using ColdFusion Extension wizards
- Value Objects and Model Objects
- Flex Framework
- Cairngorm Deepdive
- Cairngorm Over-Simplified
- Cairngorm Videos Available as FLV Downloads
- Carinform Diagram Explorer
- Core J2EE Pattern Catalog
- Flex Architecture Basics Models and Data Transfer Objects
- Getting Started with Cairngorm Part 1
- Getting Started with Cairngorm Part 2
- Getting Started with Cairngorm Part 3
- Getting Started with Cairngorm Part 4
- Getting Started with Cairngorm Part 5
- Great Cairngorm Slides from 360Flex Europe
- Introducing Cairngorm
- Steven Webster Part 1 Introducing Cairngorm
- Steven Webster Part 2 Keeping state on the client
- Steven Webster Part 2 Keeping state on the client 2
- Steven Webster Part 2 Keeping state on the client 3
- Steven Webster Part 3 Architecting the View
- Steven Webster Part 4 Feature driven development 1
- Steven Webster Part 4 Feature driven development 2
- Steven Webster Part 5 Server side integration
- Steven Webster Part 6 Rapid and consistent development with Cairngorm and Flex
- Game Development
- General Topics
- Git
- godot
- Godot Sample Applications
- Java
- Javascript
- jQuery
- Lynda.com
- Flash Professional CS5: Creating a Simple Game for iOS Devices with Todd Perkins
- Beginner's Digital Art Tutorial 01 - THE SKETCH
- Building a Mobile App with Feathers and Starling
- Building Flash Games with Starling with Lee Brimelow
- Distributing iOS Applications Through the App Store with Bill Weinman
- DSLR Video Tips: Cameras & Lenses
- Final Cut Pro Essential Training
- Flash Professional CS5: Animation Projects with Paul Trani
- Flash Professional CS5: Code Snippets and Templates in Depth with David Gassner
- Flash Professional CS5: Creating a Simple Game for Android Devices with Paul Trani
- Flash Professional CS6 Essential Training
- HTML5 Game Development
- Illustration Essential Training
- iOS App Development with Swift Essential Training with Simon Allardice
- Mac OS X Yosemite Tips and Tricks with Christopher Breen
- Making of digital Cartoons Dr. Ashraf Hamdi
- Motion 5
- Objective-C Essential Training with Simon Allardice
- Presentation Fundamentals
- Simple Game for Android Devices with Paul Trani
- Teach Kids Programming with iOS with Todd Perkins
- WordPress DIY: Small Business Website
- Mac Tips and OS X related
- MySQL
- Converting Lating 1 to UTF8
- Error: Connection (caching_sha2_password)
- How to dump mysql data
- How to increase date using ADD_DATE function
- How to install MySQL on Mac
- How to Start MySQL
- How to uninstall mysql on Mac
- Installing MAMP version for apache, mysql and php all together
- Installing MySQL Separate Components on Mac OS X
- lynda.com Lecture note for MySQL
- MySQL command list
- Setting up apache config on Mountain Lion after upgrade
- Papervision3D
- Perl
- PHP
- Codeigniter
- Cross-Site Request Forgeries, Session timeout
- Database connection and handlings
- Design Pattern
- Escape Values for MySQL
- File upload configuration
- How to enable FTP on OS X
- How to install PEAR and PHPUnit on Mac
- How to install php on Mac OS X
- How to Read The Google Chrome Cookies File on a Mac
- Installing ZendDebugger for PHP in Mac OS X Snow Leopard
- Korean Character Encoding Setup
- Object Oriented PHP and Basic Concept
- Open Source Email Marketing Software
- PDO Turotial from phppro.org
- PHP Frameworks
- PHP Objects, Patterns, and Practice by matt Zandstra
- PHP related resources and open source application
- PHP Tutorial: PayPal Instant Payment Notification (IPN)
- PHP Tutorial: PayPal Payment Data Transfers (PDT)
- PHP with Eclipse
- PHP with MySQL Beyond the Basic
- Sending Email with local server or using Gmail
- Subversion related commands
- Trouble Shooting and Error
- Wordpress: How to change table prefix
- PyroCMS
- Resource Center
- Address in Korea
- Aiseesoft Mac FoneTrans
- AnyTrans for Mac
- AppGeeker FoneTrans (Iphone Transfer)
- Audio Hijack
- bashrc dev profile
- Beauty Box
- Canon PIXMA MX922
- Carbon Copy Cloner
- citi
- Content Management Resource
- Drexel University Degree Verification Certificate
- Edwards Web Developer Site
- Essential Eclipse Shortcuts
- Essential Textmate Shortcut and Plugin
- Finale
- Free Converter mp3 mp4
- Free MP4 Converter - All to mp4
- Glyph Design
- hanbit.us production database connection
- How to create disk image (iso file) using Disk Utility on Mac
- How to host web server on your Mac
- How to rip DVD
- How to uninstall Xcode
- HP Printer
- iMac White Screen Death Fix
- Informatica Powercenter 8.6.1 download
- iTube Studio
- Jobs that I am interested in
- Korean Air - Skypass
- LOGINS
- Mac DVDRipper Pro
- Melodyne
- Microsoft Office
- My Favorite IDE
- old jongha.com 208.112.25.124
- Resource Center - Software Subscriptions
- Resume
- Shell script and Perl from eBay
- SmartGod
- STATCOUNTER check your traffic report
- TexturePacker
- Top 10 Open Source Bug Tracking System
- United Air MilagePlus, JetBlue Mileage Numbers
- VirtualHostX 7
- vmware fusion
- VPN Express
- window 7 product key
- Wondershare Unicoverter
- Wordpress 3rd Party Plugin
- www.bullisphoto.com
- www.emmahwang.com
- www.jongha.com
- www.jwebby.com
- www.koreansalon.com
- www.raddarch.com
- 쏘셜
- Unix
- Video Game
- Wordpress
- Backup
- Elegant Themes
- Good Theme Sites
- Good Wordpress Plugins
- lynda.com - Creating Child Theme
- lynda.com - Creating Custom Theme
- lynda.com - Widget and Plungin
- lynda.com Login
- Professional WordPress Plug-in Development
- Resource Links
- Security Settings
- Smashing WordPress - by Thord Daniel Hedengren
- Tips and Solutions
- Wordpress FTP credential problem
- Actionscript
- Cooking
- Amazing Food 관련 비디오
- American Food
- Brussels sprout
- Caramel Sauce
- Chocolate Sauce
- Donuts - 영화-하와이언레시피의 도너츠만들기[말라사다:빵.베이킹] malasadas
- Eggs in hell - honeykki 꿀키
- Fresh Tomato Recipe: Baked Parmesan Tomatoes
- Grilled Chicken Sandwich, Fried Chicken Sandwich
- Hamburger Patty
- Homemade Pizza Recipe - Home Cooking Adventure
- How to Make Polish Sausage: Bob Borkowski Style
- Jamie Oliver - How to Cook Perfect Steak
- Jamie's Crispy Fried Squid
- Jamie's Perfect Roast Potatoes
- Macaroni and Cheese
- Meatball
- Pizza - honeykki 꿀키
- Roasted Potato & Cheese Tater Tots Recipe - Home Cooking Adventure
- Scallops
- Slow-Roasted Tomatoes, Oven-roasted tomatoes with garlic & lemon thyme
- Stake Sauce
- Steamed Clams
- Tomato Salad - Jamie's Ultimate Tomato Salad
- 길거리 토스트 - Honeykki 꿀키
- 댕기피자빵 :daenggi pizza bread
- 블루베리스콘: 베이킹]Blueberry scones
- 식빵 만들기
- 치즈 오븐 스파게티 - Honeykki 꿀키
- 팬케이크(Pancake) - Honeykki 꿀키
- Cooking Recipe
- Aeri's Kitchen
- Buttermilk Fried Chicken
- French Fries - How to Make Crispy French Fries
- French Toast
- Grilled Shrimp
- How to make Chow mein
- Japanese Food - Shish Rice, Hand Roll, California Roll
- Shrimp Scampi
- Shrimp Tempura
- Shusi and Sashimi cutting
- 가지무침 얼큰 닭곰탕
- 감자탕
- 고사리나물 볶음
- 궁중떡복기
- 닭볶음탕 - Spicy Chicken with Vegetables
- 동그랑땡
- 돼지불고기
- 멸치볶음
- 물냉면 비빔냉면
- 불고기
- 비빔밥
- 산적
- 삼계탕 - Traditional Korean Chicken Soup
- 샤부샤부
- 숙주나물
- 순두부 찌게
- 양념통닭
- 오이 냉국 - Cold Cucumber Side-dish
- 오이지 무침 - pickled cucumber side-dish
- 오징어콩나물찜 and 애호박버섯조림
- 월남국수
- 육계장
- 이탈리아식 애호박 팬케이크
- 잡채
- 잣죽
- 잦죽 만들기
- 제육볶음
- 짬뽕
- 찐빵 and 야채찐빵
- 탕수육
- 팥죽
- 해물파전
- 호박전
- Honeykki 꿀키
- Italian Food
- Japanese Food
- Kids Lunch Ideas
- 빵만들기 - Baking관련
- 요리관련 상식
- 우리의식탁 W TABLE
- 5 Sandwiches for Picnic
- 7 Korean Side Dishes (반찬) - 감자볶음, 가지볶음, 마늘종 새우볶음, 고구마줄기, 취나물, 콩장
- 7 Korean Side Dishes (반찬) - 양배추 겉저리, 감자햄 볶음,
- Chicken & Egg in Hell
- Folded Kimbap (네모 김밥)
- Korean birthday party food (미역국, 잡채, LA갈비, 양배추 겉저리)
- 불고기비빔밥
- 고추장 제육복음, 고추장 삽겹구이
- 봄 제철요리 4가지
- 삽겹살 김밥, 삽겹살 김치말이, 쭈꾸미 살볍살
- 치즈 닭갈비
- 중국요리
- 최고의 요리비결
- 김덕녀, 잔치국수와 비빔국수
- 김막업, 닭죽과 톳무침
- 김영빈, 해물짬뽕과 노각피클
- 김인숙, 도토리묵냉채, 녹두전
- 김인숙, 보쌈정식, 물김치
- 김인숙, 소고기국밥과깍두기
- 김인숙, 제육볶음과 호박새우찌개
- 김하진, 일본식돈가스
- 박경신, 만두전골 (김치만두 만두는법)
- 박경신, 부추물만두와 군만두
- 방영아, 버섯전골 (소고기), 김무침
- 윤숙자, 소갈비찜과 과일나박김치
- 이명자, 닭곰탕 (삼계탕)과 김치당면볶음, 닭계장
- 이명자, 매운사태찜과 새우피망볶음
- 이명자, 버섯불고기와 배추겉절이
- 이명자, 쟁반냉면과 여름동치미
- 이종임, 고등어조림과 고구마줄기나물
- 이종임, 고추장돼지불고기와 검은깨두부냉채
- 이종임, 된장찌개, 양배추말이쌈밥
- 이종임, 뚝배기불고기, 풋고추장아찌
- 이종임, 보쌈김치
- 이종임, 사골해장국과 오이지
- 이종임, 삼계탕과 새송이장아찌
- 이종임, 열무김치
- 이종임, 육개장과 현미수수밥
- 이종임, 전복수삼밥과 단호박낙지볶음
- 이종임, 총각김치와 파김치
- 이종임, 통배추김치
- 이종임, 해물순두부찌개, 버섯양파볶음
- 이혜정의 치킨데리야끼
- 임미자, 매콤깐풍기와 연근무침
- 임미자, 북어콩나물국밥과 바삭채소튀김
- 임효숙, 닭볶음탕, 애호박부침
- 임효숙, 닭볶음탕, 애호박부침
- 정미경, 모시조개된장국과 넓적깍두기
- 정미경, 부대찌개와 멸치무조림
- 정수주, 깐풍기와 쌀국수볶음
- 정수주, 새우마요네즈와 삼선짬뽕
- 정수주, 탕수육과 자장면
- 정신우, 꽃게된장국과 콩나물버섯무침
- 최인선, 오징어콩나물국, 화산달걀찜
- 한복선, 감자탕과 머위들깨볶음
- 한국음식
- 갈비찜 백종원
- 갈비찜 백종원
- 갈치 무조림
- 감자조림
- 계란말이 (달걀말이)
- 김 굽는방법
- 김치말이 국수
- 김치찌게
- 깍두기 - 이순옥의 최고의 요리비결
- 꽃게해물탕 - 이순옥
- 녹두전, 녹두빈대떡
- 닭죽
- 마파두부
- 만두전골
- 메밀 비빔국수
- 멸치볶음 (매콤한 큰멸치)
- 멸치볶음 (작은멸치)
- 박경신의 소고기영양죽과 단호박전
- 배추겉저리 (김장배추)
- 배추겉저리 (얼갈이김치)
- 배추김치 - 이순옥의 최고의 요리비결
- 백김치 - 최고의 요리 비결 이순옥
- 보쌈, 양념새우젓
- 볶음밥
- 부대찌게 - 요리연구가 박경신
- 부추전 - 바삭바삭 튀김같은 전 만드는 방법
- 비빔국수
- 사골우거지국
- 소고기 육계장 - 이순옥
- 수제어묵 - honeykki 꿀키
- 시금치 나물 무침
- 알타리김치, 총각김치 - 이순옥
- 애호박 간장국수
- 애호박 무침
- 열무냉면
- 오이냉국, 오이무침
- 오이소배기, 오이소박이
- 오이지
- 오징어국 오징어무국
- 오징어볶음
- 우거지 갈비탕 or 갈비탕
- 잔치국수
- 전복죽
- 전복해물뚝배기 + 제육복음(돼지고기 목살)
- 정월대보름 음식
- 제육볶음
- 찐빵만두
- 착한 곰탕집의 착한 곰탕 조리 비법
- 찰밥
- 콩나물국밥
- 탕평채(복잡한)
- 튀김처럼 바삭한 김치전
- 파김치 - 이순옥
- 팥밥, 팥 찰밥, 전통식 찰밥찌는 법
- 풋배추, 얼간이 김치 - 한복선 최고의 요리비결
- 핫도그
- 해물파전 - 이순옥
- 황태콩나물국과 두부조림 - honeykki 꿀키
- 한국음식 2
- Dance
- Economics and Investment
- 2020 차이나 리포트
- 23 Things They Don't Tell You About Capitalism (장하준)
- A Little History of Economics
- 1. Cool Heads and Warm Hearts
- 10. Workers of the World
- 11. A Perfect Balance - William Jevons(Marginal Utility)
- 13. The Profits of War
- 2. The Soaring Swans
- 29 - Money Illusion
- 3. God's economy (Medieval Economists)
- 4. Going for Gold
- 5. Nature's Bounty
- 6. Invisible Hands (Adam Smith)
- 7. Corn Meets Iron
- 8. An Ideal World
- 9. Too Many Mouths
- Divorce in California
- Economic Terms (경제관련 용어)
- Economics - The User's Guide (장하준)
- Economics General and Miscellaneous (경제관련상식)
- Economists
- Adam Smith
- Alfred Marshall
- Arthur Pigou
- David Ricardo
- François Quesnay (French, Physiocrat 중농주의, 1694)
- François Quesnay (Physicratist 중농주의 1694 ~ 1774)
- Friedrich Hayek (Austrian School)
- Henry George (The Single Tax)
- Jean-Baptise Say
- John Maynard Keynes
- John Stuart Mill
- Joseph Schumpeter (Austrian School) - Creative Desruction
- Thomas Robert Malthus
- Tax
- The Psychology of Money - Morgan Housel
- The Simple Path to Wealth - JL Collins
- Wealth of Nation - Adam Smith
- 경제학 강의
- Lecture 1: 아담 스미스 : 경제학의 시작
- Lecture 10
- Lecture 10 - 알프레드, 마샬 차가운 이성, 뜨거운 심장
- Lecture 2: 멜서스: 우울한 경제학자의 우울한 세상읽기
- Lecture 3: 리카르도1: 고전경제학의 슈퍼스타
- Lecture 4: 리카르도 2 비교우위란 무엇인가?
- Lecture 5: 리스트 후진국 독일의 열렬한 경제학자 (Friedrich List)
- Lecture 6 - 부르마불게임의 종말 (Henry George) - American Economist
- Lecture 7 - 월가는 왜 자본론을 읽는가 1
- Lecture 8 - 월가는 왜 자본론을 읽는가 12
- 김수행 - 케인스의 ‘국가만능주의’는 위기 해결 못해
- 장하준 - RSA ANIMATE: Economics is for Everyone!
- 장하준의 경제학 제 1편 우리가 경제학을 알아야 하는 이유
- 돈의 속성
- Andre Kostolany
- Benjamin Graham
- Howard Marks
- 가난은 생각보다 훨씬 더 잔인하다 - 빌게이츠
- 경제 전문가는 경기를 예측할 수 있나?
- 내가 청년으로 다시 돌아가 부자가 되려 한다면 - 주식투자
- 달걀을 한 바구니에 담지 않았는데 왜 모두 깨질까?
- 돈마다 시간은 다르게 흐른다
- 돈은 인격체다
- 리스크가 클 때가 리스크가 가장 작을때다 - 인문학적 이해 (워런 버핏)
- 반복되는 운은 실력이고 반복되는 실패는 습관이다
- 부자가 되는 세가지 방법
- 빨리 부자가 되려면 빨리 부자가 되려 하면 안 된다
- 삼성전자 주식을 삼성증권에 가서 사는 사람
- 정기적 수입 == 100배 규모의 자산
- 투자는 예측해서 하는 것이 아니라 벌어진 상황에 대해 대응하는 것이다
- 만화로 보는 맨큐의 경제학(Principles of Economics)
- 부의 재편
- 비쥬얼 경제사 (Visual Economics) - 송병건
- 비쥬얼 경제사 1 (송병건)
- 1. Alexander The Great from different cultures
- 10. The Expansion of Russian Empire toward Siberia
- 11. Napoleon and Sphinx
- 12. Slave Trade from Africa
- 13. Industrial Revolution and the Accidents from it
- 14. Great Britain and World's Fair
- 15. Irish Potato Famine (악마의 식물)
- 16. Japan beyond Asia
- 17. The Beginning of the Travel Agency
- 18. The Extinction of Buffalo in America
- 19. Colonized India and Railroad Business
- 2. Silk road
- 20. American Monopolists (미국 대기업의 폐해)
- 21. France and Germany (프랑스 흡혈귀)
- 22. Santa Clause, from saints to the symbol of commercialism
- 3. 장거리 무역의 귀제 (Islam Caravans)
- 4. Pax Mongolica - The Spread of new disease
- 5. Maroco Polo - The Travels
- 6. The Fall of Constantinople
- 7. Japan-Chosun War(임진왜란) and Slave trade
- 8. Paper Revolution
- 9. Tulip Bubble
- 유한계급론 (Sociology) - 소스타인 베블런
- 이게 경제다(최배근)
- 청소년을 위한 국부론 - 김수행
- 행동경제학(Misbehaving) - Richard Thaler
- Education
- ChineseClass101.com
- Element - Talents meet passion - Ken Robinson
- Everyday Chinese
- How to Speak How to Listen - Mortimer J. Adler
- Palgrave Study Skill Handbook - Stella Cottrell
- Proust and the Squid - Marryanne Wolf
- Reader, Come Home - Maryanne Wolf
- Socratic Circle - Fostering Critical and Creative Thinking
- The Aims of Education - Alfred North Whitehead
- The Education of Karl Witte; Or, the Training of the Child
- The Paideia Program - An Educational Syllabus
- The Paideia Proposal - An Educational Manifesto
- The Problem of American Education
- The Well-Trained Mind - A Guide to Classical Education - Susan Wiser Bauer
- Wilhelm Von Humboldt - German Education
- You, Your Child, and School: Navigate Your Way to the Best Education - Ken Robinson
- 내 아이를 위한 칼비테 교육법
- 리딩으로 리드하라 (Lead by Reading)
- 문정아 중국어
- ChineseClass101.com
- Essays and Writings
- Date App Notes
- Love and Marriage (사랑과 결혼에 관한 나의 생각들)
- Dating App에 의한 연애 문화
- How I came to US
- Menopause and Marriage (페경과 부부생활)
- Refuse to Sex, Sex an Emotional Connection
- The Reason Why I don’t Want to Go Back to Work
- The Reason Why My Wife Became Workaholic
- The Reason Why My Wife Feels Unfair
- Why women file for divorce more than men
- Why Women with Dog
- Women need emotional connect but not men
- 결혼도 사랑의 힘 이혼도 사랑의 힘
- 결혼예찬 vs. 이혼예찬
- 공주병
- 공주병 (English Research)
- 그녀와 헤어지게 된 이유
- 기독교사 성윤리에 끼친 부정적인 영향
- 나의 이혼에 관한 사회경제학적 분석
- 남자 피 말리는 여자
- 남자가 줄서있는 여자의 비극
- 내가 아내를 사랑하지 않는 이유
- 내가 아내의 이혼 요구를 수락한 이유는
- 내가 절대 사랑할 수 없는 여자
- 눈높이를 낮춘다는 표현의 철학적 의미
- 니체가 말하는 Resentment(르상티망)와 이혼하는 부부관계
- 바람피운건 이혼사유가 되서는 않됀다.
- 사람들이 이상형을 기다리는 이유
- 사랑없는 성관계가 불결하다고 생각하는 여자의 심리
- 사랑하면 라면만 먹고도 살수 있는 이유?
- 아내에게 화가나는 이유
- 아내와 헤어지게 된 이유
- 여자들이 성관계 거부를 무기로 사용하는 이유
- 연애때는 문제가 않보이다가 결혼하면 보이기 되는 이유
- 이혼한 중년 여성들이 재혼이 힘든 이유
- 정신적인 사랑, 관념적인 사랑은 아름다운 시로 표현되곤 한다.
- 정신적인 사랑은 아름다운 시로 표현되곤 한다. 예술은 고독에 대한 자기 방어적 표현이다.
- 중세시대의 육체적 사랑에 대한 인식과 현대인의 인식 비교
- 질투라는 감옥
- 첫사랑이란 우리가 생각하는 그런 사랑은 아니다
- 한번도 차여 본적이 없는 여자
- 혼자사는 여자와 금욕주의
- Virtue, Character (덕성과 인격)
- 공주병 관련 Research
- 5 Reasons Why Dads Are Important to Their Daughters
- 5 Ways Narcissists Damage Loving Relationships
- Narcissism and partner-enhancement at different relationship stages
- Narcissistic personality disorder
- Shades of narcissistic love: Relations between narcissism dimensions and love styles
- 공주병 관련 이미지
- 공주병있는 Sexual Partner
- 남자와 헤어짐을 제데로 경험하지 못한 경우 (Detachment)
- 아버지의 딸 (아버지와 딸의 관계)
- 올바른 성문화 - 동양과 서양의 성문화 비교
- 글 쓰기의 최전선 (은유 - 김지영)
- 글쓰기 관련 책
- 기독교 관련
- 나의 삶에 관해
- (email) - 글쓰기를 통해 내 생각과 감정을 알게된 사례
- MBTI F와 T로 사랑을 한다는 것
- Reason for applying the program
- We didn't have to do thi
- 교회오빠의 부부관계
- 그건 그거고 이건 이거다 (섹스는 섹스고 사랑은 사랑이다)
- 그녀가 20대후반 40대 중년 남성이랑 바람을 피운일
- 김어준과 같은 반항적 멘탈이 형성되기 위한 성장환경
- 내가 결국 그녀를 선택 할수 없었던 이유
- 내가 여자한테 사랑을 표현하는 방법
- 느낌은 생각보다 정확하다
- 대구를 방문하는 일이 배려가 아니다. (주제파악 좀 하세요)
- 데이트 도중
- 돌싱녀와 미혼여성의 차이
- 루소와 나의 독서법
- 만날땐 좋은데 헤어지면 싫어지는 여자
- 미국 이민자로 살아갈때 느끼는 갈등
- 미국에서 만날땐 좋았는데 한국에 오니 현실적 문제가 갈등으로 들어나는 이유
- 사랑 그 어리석음의 강점
- 사랑도 원칙데로
- 사랑없이 사랑에 관한 글을 쓴다는 것은
- 사랑의 언어 vs. 결혼의 언어
- 살면서 어려운 결정을 내린다는 것의 의미
- 실존주의를 모른 채 실존주의로 살아온 나
- 아내랑 이혼하게 된 이유
- 아빠의 만료된 여권
- 아쉬울게 없잖아
- 아이들 옷을 산 실수
- 연애는 많이 해봤는데 사랑은 해보지 못한 여자
- 연애의 복기(復棋)
- 인문학적 영성과 종교적 영성
- 자기합리화의 습관화
- 적어도 내가 깨닭은 두가지 실수
- 절교를 무기삼아 자신이 원하는 걸 얻다보니 결혼이 불가능했다
- 피해의식(Victim Mentality) 정신질환과 인간관계
- 한국에서의 연애와 미국에서의 연애
- 한국을 떠난다는 건
- 다가오는 말들 (은유)
- 리치브릿지 - 나는 자수성가 부자와 결혼했다
- 브런치(Brunch)
- 사랑과 섹스에 관하여
- 싸울땨 마다 투명해 진다 (은유 - 김지영)
- 쓰기의 말들 (은유) - 안쓰는 사람이 쓰는 사람의 기적이 되기 위하여
- 종하의 아침놀
- 좋은 에세이 모음
- 집샤님의 글
- 효진님의 글
- Farming and Gardening
- Friedrich Nietzsche
- Fuller Seminary
- NE502 - Hermeneutics
- OT501 - Pentateuch
- Diffefference between Ten Commandments in Exodus and Deutronomy
- Dr John¡¯s Guide to Old Testament Study
- Dr John¡¯s Guide to Old Testament Study
- Eve and Adam: Is a feminist reading possible?
- Feministinc interpretation of 1 Timothy 2:11~14
- Fuller related information and Portico
- Genesis Narrative Structure and Repeating Patterns
- How Could God Command Genocide in the Old Testament?
- New Horizons - My Memories of Edward J. Young
- Parental Favoritism and Sibling Rivalry
- Women pastors / preachers? (1 Timothy 2:11-15)
- OT502 - Prophets
- PH510 - Christian Apologetics
- Arguments for the Existence of God
- Basic Apologetics by Art Lindsley
- C.S. Lewis¡¯ illustration about different perspective from Meditation in a Toolshed
- Cain's Wife, who was she?
- Christianity and Culture by J. Gresham Machen
- Critics of Presuppositionalism
- Darwin's Theory of Evolution
- Faith and Reason
- handbook of Christian Apologetics
- Heresies in Early Church
- How Accurate Is The Bible?
- How to Get Apologetics in Your Church
- Is the Bible truly God's Word?
- Love Your God With All Your Mind - J. P. Moreland
- Postmodernism and C.S. Lewis
- Presuppositional Apologetics
- The Canonicity of the Bible
- The Hegelian Dialectic and The Third Wave Synthesis part 1
- The Mind's Role in Spiritual Transformation by J. P. Moreland
- The Resurrection of Jesus: Did he really rise from Dead?
- The Toulmin Model of Argument
- Why Believe in Miracles? by Ken Boa
- Why would anyone believe that Jesus actually rose from the dead?
- Research Paper Related
- Critical Response results from interacting with ideas
- Critical Response Structure
- Fuller Mdiv Required Courses
- How to write critical response
- Skills Team Hull University - 1. Reflective Writing
- Skills Team Hull University - 2. 5 minute essays
- University of Hull (Writing skills and Academic Study Guides)
- Writing fixes
- ST501 - Systematic Thelology 1
- ST502 - Systematic Theology 2
- ST503 - Systematic Theology 3
- Alister McGrath - Eschatology Introduction
- Helmut Thielicke - Ethics and Eschatology
- It is well, with my soul - Horatio Gates Spafford
- John Zizioulas - Being as Communion - Book Summary
- John Zizioulas - Communion and Otherness
- John Zizioulas - Communion Ecclesiology
- Lecture Note #1
- Lecture Note #2
- Lecture Note #3
- Lecture Note #4
- Major Theologians and Pictures
- Miroslav Volf - After Our Likeness
- Miroslav Volf - Participatory Ecclesiology
- Moltmann, The Coming of God
- Moltmann, Theology of Hope
- Placher - Why bother with church?
- Sacrament
- ST503 Research Paper #1 - Ecclesiology
- ST503 Research Paper #2 - Eschotology
- Stanley Granz - The Doctrine and Ministry of Church
- subjectivistic pietism
- ST511 - Orientation to Theological Study
- Bibliography for research paper
- How to read a book 1 - Dimensions of Reading
- How to read a book 2 - The Third Level of Reading : Analytical Reading
- How to read a book 3 - The fourth level of reading : Syntopical Reading
- How to Read a Book by Mortimer Adler ► Animated Book Summary
- How to think theologically 1
- How to think theologically 2
- Lecture 2: Gathering a Tentative List of Resources
- Research Paper : Comfort Zone As Barrier to Church Growth
- The Comfort Zone by Lura Langenback
- ST574 - C.S. Lewis
- A Chronology of Important Dates in the Life of C.S. Lewis
- Art Lindsley - C.S. Lewis on Chronological Snobbery
- Art Lindsley - C.S. Lewis's Absolutes
- Art Lindsley - C.S. Lewis's Obstacles to Faith
- Art Lindsley - C.S. Lewis's Seven Key Ideas
- Art Lindsley - The importance of Imagination
- C. S. Lewis: A Profile of His Life
- C.S. Lewis: His Life and Works
- Characteristics of premodernism, modernism and postmodernism
- Christian Apologetics by C.S. Lewis
- Class Note #1
- Class Note #2
- Class Note #3
- Course Materials
- Douglas R. Groothuis - Apologetics between C. S. Lewis and Francis Schaeffer
- Earl Palmer - Evangelism Takes Time (1985)
- Earl Palmer - The Man, The Idea and The Journey
- Grief Observed Summary
- Grief Observed Summary and Analysis
- Humphrey Carpente - C. S. Lewis: Myth and Conversion
- Key Components of Lewis's View of Scripture
- Links
- Man or Rabbit? By C.S. Lewis, from God in The Dock
- Research Paper #1 - C.S. Lewis on The Scripture
- Research Paper #2 - C.S. Lewis's Apologetics
- Study Guide on Reason
- The Abolition of Man Summary
- The Difference between Allegory and Symbolism
- What is metanarratives?
- 종의 기원 Origin of Species
- Golf
- Golf with Amiee
- M Club Golf
- Short Game
- [고덕호레슨]딱 네 개로 정리한 어프로치 실수 방지법
- Tiger Woods Chipping and Wedge Lesson Compilation
- Tiger Woods Practice around the green
- Tiger Woods, Rory McIlroy & Jason Day Short Game Session
- 박인비 퍼팅
- 박인지 코치의 short game shot
- 박희영 Steve Barn
- 임진한 퍼팅의 기본
- 최나연 - High Chip Shot
- 최나연 - 박힌볼 벙커샷, 기본벙커샷
- 최나연 - 오르막 chip shot, 허리열어주기
- Swing Lessons
- [골짤강] 코어를 이용한 장타
- Amiee - Hinging
- Back Swing Top
- Driver
- Golf Swing Theory
- HPGA - 골프 다운스윙때 오른쪽 팔꿈치, 겨드랑이 붙여야 하나요
- HPGA - 공잘마추는 방법 (기본기 - 몸안쪽에)
- HPGA 골프아카데미 - 드라이버는 손목을 풀어야한다.
- Lydia Ko Swing
- Tiger Woods - Drills
- WorldClassGolf - Why Amateur Golfers can’t create Compression
- Writs(손목사용)
- 경사지 레슨의 끝판왕, 모든 경사지 스윙의 공식표
- 김남기프로 - Takeaway, 오른쪽어깨 열어주기
- 김남기프로 - 몸통회전, 척추를 중심으로 위에서 아래로
- 김대현프로의 드라이버 노하우! 아주 기초적이며 디테일한 내용. [심짱의 나드짱]
- 백스윙 (Back Swing)
- 신준프로 - 헤드를 잘 닫으면 얻는 것 (Supination)
- 엎어치는 스윙교정
- 오지인tv - Early Extension
- 오지인tv - 다운스윙 손목외전 수피네이션
- 오지인tv - 왼쪽어깨 올리지않기
- 오지인tv - 제데로된 Hip turn sequence, 꼬리뼈위치
- 오지인tv - 지면반력 제데로 이해하기
- 왼쪽골반, 골반은 뒤로빠져줘야
- 유소연 - 경사진 라이, 내리막 라이
- 이시우 프로 - 아이언샷 셋업 시 발바닥에 집중
- 장은비 - 골반 움직임을 배워봐요
- 장은비 - 드라이버 슬라이스 잡기
- 장은비 - 왼쪽만큼 오른쪽도 중요 ! 오른쪽 사용법 레슨
- 하체의 움직임 - Hip Turn
- Videos and Lessons
- Workout
- 레슨테크트리(Lesson Tech Tree)
- 박진이 프로, 고경민 프로 (SBS Golf)
- 박진이 프로 - 클럽헤드 던지기 (이시훈 프로, Mclub 골프)
- 고경민 프로 - 아이언, 내려치지 못하는 당신을 위해 준비했습니다
- 고경민 프로 - 클럽던지기, 배로 튕겨주기
- 박진이 프로 - Wood Shot
- 박진이 프로 - 가파른 Attack Angle
- 박진이 프로 - 과도한 아웃-인 궤도 교정으로 쌩크와 이별하기
- 박진이 프로 - 다운스윙 팔 내리기
- 박진이 프로 - 박진이 프로 레슨 한번에 비거리 40m 늘어난 골퍼, 이제 250m 가즈아
- 박진이 프로 - 백스윙때 체중이 약간 왼쪽으로
- 박진이 프로 - 비거리 늘리는 파워스윙! 오른다리 잡아두기
- 박진이 프로 - 오른쪽 스윙, 왼쪽 스윙
- 박진이 프로 - 오른팔 (Setup)
- 박진이 프로 - 왼발뒤쪽에 체중이 실려야한다
- 박진이 프로 - 유연한 회전을 방해하는 요인들 교정하기
- 박진이 프로 - 쭉 뻗는 팔로우 스루①머리의 움직임
- 박진이 프로 - 클럽헤드 잘 던져서 비거리 향상! (왼쪽 겨드랑이)
- 박진이 프로 - 파워스윙
- 박진이 프로 - 하체의 반동 이용하면 급해지는 스윙 고칠 수 있어요
- 박진이 프로 - 헤드무게 느끼면서 Take away 하기
- 박진이 프로 - 회전이 안 되는 이유..뻣뻣한 팔의 움직임
- 빵빵쭌프로
- 스윙닥터 김남기프로
- 안소영프로
- 유프로 왕초보 골프배우기
- 이시우 프로
- 이현프로 (SBS Golf)
- 이현 프로 - 클럽 헤드를 던지는 꿀팁
- 비거리를 늘리고 싶다면 볼을 눌러 치자! (왼손 그립)
- 이현 프로 - 가까이 하기엔 너무 먼 우드... 우드랑 친해져요!
- 이현 프로 - 공을 강하게 치는 법 스윙 편 (No Spin, Flat Square Impact)
- 이현 프로 - 새해에는 나도 장타자! 장타왕!
- 이현 프로 - 시청자분들한테만 알려드리는 임팩트 비밀!
- 이현 프로 - 임팩트시 손목의 비밀
- 이현 프로 - 헤드 스피드, 뒤에서 던지면 스피드 UP (손등이 공을 바라보게)
- 이현 프로 - 헤드는 항상 손보다 위에. 왼손그립을 눌러서 잡아라
- 임연석 프로
- 임진한 프로
- 장은비 프로
- 조윤성프로
- ** 조윤성프로 - 오른쪽 골반에 따른 엄청난 스윙의 차이
- ** 조윤성프로 - 좋은 스윙에는 반드시 두 가지 당김이 있습니다
- ** 조윤성프로 - 지면반력
- 조윤성 프로 - 광배근을 선택하자. 손이 아니라 갈비뼈
- 조윤성 프로 - 오른쪽 어깨의 움직임 (최대룡 프로)
- 조윤성프로 - Driver, hands-up backswing
- 조윤성프로 - Early Extension 고치기
- 조윤성프로 - How to make a golf impact
- 조윤성프로 - inside out 괘도만들기는 힙턴 backswing
- 조윤성프로 - Takeaway, Hinging, Coking
- 조윤성프로 - The two key elements of Golf Swing Transition
- 조윤성프로 - 간단히 배우는 던지는 스윙의 원리
- 조윤성프로 - 골퍼의 99%는 Two Plan Swing
- 조윤성프로 - 다우스윙시 힙뒤로, 척추각유지
- 조윤성프로 - 던지는 스윙을 위한 단계별 접근방법
- 조윤성프로 - 드라이버 끌고 들어오면 폭망, 릴리스타이밍 알기
- 조윤성프로 - 드라이버 오른쪽 팔꿈치 유지하기
- 조윤성프로 - 드라이버 임팩때 왼속목 펴주기, 그리고 던지기
- 조윤성프로 - 드라이버, 오른팔꿈치 역할, 필드에서 드라이버가 잘 안 맞는 이유
- 조윤성프로 - 드라이버, 이대로만 쭉 유지 할 수 있다면
- 조윤성프로 - 드라이버, 헤드높이를 낮게, 힘빼고 툭떨어지게
- 조윤성프로 - 백스윙 프로처럼 하는 법
- 조윤성프로 - 빼야될힘과 필요한힘
- 조윤성프로 - 상체가 뒤에 남아야 클럽을 던질수 있다
- 조윤성프로 - 손이 바깥으로 나가는 경우
- 조윤성프로 - 스윙의 넓이가 중요. 백스윙때 오른팔을 넓게
- 조윤성프로 - 아이언 Impact Angle, 어떤 각도로 클럽이 들어와야하나?
- 조윤성프로 - 아이언, 손목의 모양, 힌지, 코킹
- 조윤성프로 - 아이언, 열렸다가 닫혔다가 하지말고
- 조윤성프로 - 아이언은 눌려쳐야한다
- 조윤성프로 - 오른쪽 다리 쭉 밀어준다
- 조윤성프로 - 오른쪽 무릎 굽힘유지 (정면유지)
- 조윤성프로 - 오른쪽 팔꿈치가 중요한 이유
- 조윤성프로 - 오른쪽 팔로 클럽받쳐주고 어깨 힘빼고 클럽던져주기
- 조윤성프로 - 오른쪽으로 골반 sway 척추각도 무너지기
- 조윤성프로 - 왼쪽무릎사용하기
- 조윤성프로 - 왼팔의 회전과 움직임
- 조윤성프로 - 이렇게 하면 백스윙은 프로수준!
- 조윤성프로 - 전환동작을 잘해야 진정한 고수(Transition)
- 조윤성프로 - 제대로 던져 질 때의 손 맛을 느껴보다
- 조윤성프로 - 팔을 내려주면서 몸통회전을 적극적으로
- 조윤성프로 - 힘빼고 던지기
- 조윤성프로 - 힙턴 반드시 해야 합니다 / 방법을 알면 어렵지 않아요
- 직딩골프
- 최근 레슨
- 최나연
- 최대룡프로
- 탈골스윙
- 허석프로
- History
- 두선생의 역사공장 (YouTube)
- A Curious History of Mathmatics
- A Little History of Literature
- 14. How to read - Dr. Johnson
- 15. Romantic Revolutionaries - John Keats (1795 - 1821)
- 16. The Sharpest Mind - Jane Austen
- 2. Fabulous Beginning (Myth)
- 3. English tales - Geoffrey Chaucer
- 5. English Tales - Chaucer
- 7. The Bard - William Shakespeare
- 8. The Book of Books (The King James Bible)
- 9. Minds Unchained - John Donne (Death be not proud)
- Pilgrimage in the Middle Ages
- A Little History of Religion
- A Little History of the World - E. H. Gombrich
- 29. The Church at war - Ignatius of Loyola
- 35. The Last Conquerer - Napoleon
- A conqueror who knows how to rule - Charlemagne
- A new age - Renaissance
- A new faith - Martin Luther
- A new world - Columbus and Hernando Cortez
- A struggle to become lord of Christendom
- A truly new age - Enlightment
- A very violent revolution
- Across the sea - China, Japan, and America
- An lucky king and a lucky king - Louis XIV of France
- An Unequal Struggle - Greece and Persia
- Chivalrous Knights
- Cities and Citezens - France become strong
- Emperor in the age of chivalry - Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor
- Heros and Their Weapons - Sparta and Troy
- Life in the empire and at its frontier - Roma
- Meanwhile looking Eastward... -
- Men and machines - Industrial revolution, why in Great Britain?
- New wars and new warriors - Hannibal
- Rulers of the western world - Rome
- Sunday...Monday - Mesopotamia
- Terrible times - Thirty Years War
- The enlightened one and his land - India
- The good news - Christianity
- The great teacher of a great people - Confucius and Lao-Tzu
- The greatest adventure of all - Alexander
- The Land By the Nile - Egyptian Civilization
- The last conqueror - Napoleon
- The starry night begins
- The Storm - Migration of German tribes
- There is no God but Allah
- Two new states in Europe - Latin America Independence
- Two small cities in one small land
- American History
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Being a British Colonist
- 3. Being a British America
- 4. "Ever at Variance and Foolishly Jealous": Intercolonial Relations
- 5. Outraged Colonials: The Stamp Act Crisis
- 6. Resistance or Rebellion? (What was happening in Boston?)
- A Covenant of Courage: Anne Hutchinson
- American Revolution
- Anti-intellectualism in American Life (Who is intellectuals?)
- Battle Of Gettysburg (Full Documentary)
- Benjamin Franklin - Advice to a Young Tradesman
- Civil War - Slavery and Missouri Compromise in early 1800s
- Crash Course US History
- Four Centuries of American Education
- Lewis & Clark: Great Journey West
- Lewis and Clark Expedition Documentary
- Pragmatism
- Puritan New England (video lecture)
- Separation of Church and State - What the Founders Meant - David Barton
- The Bible, The School, and the Constitution: Guest Post from Steven K. Green
- The Declaration of Independence: A Transcription
- The Seven Years War: Crash Course World History #26
- Thirteen Colonies: the New England Colonies
- Thirteen Colonies: the New England Colonies (PowerPoint)
- U.S. Constitution part 1
- U.S. Constitution part 2
- Understanding How the Declaration of Independence and Constitution Work Together
- Understanding the Declaration of Independence - 9 Key Concepts Everyone Should Know
- US Declaration of Independence - Khans Academy
- What were the Salem Witch Trials?
- What Will Happen to America if Trump Wins Again? Experts Helped Us Game It Out.
- 미국 '영토확장의 역사' 아는척하기
- 미국의 반지성주의
- 미국이 반 지성주의 (Anti-intellectualism in American Life 1963)
- Ancient History
- Biographies
- Abraham Lincoln - Gettysburg Address
- Abraham Lincoln - 영화명장면
- Alan Turing - Mathematician, invented the first computer
- Albert Einstein - Science and Religion
- Albert Einstein - 일반상대성이론
- Benjamin Franklin - 11 Surprising facts about him
- Benjamin Franklin and his quotes
- Bismarck
- George Washington
- Jan Hus (1372 - 1415)
- Jane Austen
- John Knox
- John Witherspoon
- John Wycliffe (1331 ~ 1384)
- Joseph Stalin
- Julius Caesar
- Karl Marx - his family life
- List of Great Men and Women during Ancient Period (5000 B.C. ~ A.D. 400)
- List of Great Men and Women during Late Renaissance/Early Modern (1600 - 1850)
- List of Great Men and Women during Medieval/Early Renaissance (400 B.C. ~ A.D. 1600)
- Martin Luther - from biography.com
- Martin Luther - with painting Luther as Hercules Germanicus
- Martin Luther reformer's famous statement! (Not by Faith Alone)
- Nikola Tesla
- Queen Elizabeth
- Saint Anselm of Canturbery
- Saint Francis of Assisi
- Saint Thomas Aquinas
- Toru Iwatani (Pac Man creator)
- Who was Karl Marx?
- EBS 사회탐구
- English History (영국역사)
- British Monarchy Family Tree (Alfred the Great to Queen Elizabeth II)
- Elizabeth Woodville, The White Queen
- English Civil War - Charles I (ppt included)
- Hundred Years War
- Industrial Revolution
- Oliver Cromwell
- Puritans
- The First Georgians The German Kings Who Made Britain Episode 1
- Wars of Roses
- William Tyndale and Henry the VIII
- 영국이 강대국이 된 이유: 산업혁명 (5가지 이유)
- 청교도 혁명과 명예혁명
- European Civilization 1648 - 1945
- French Revolution
- Enlightenment Thinker - Marquis de Lafayette
- Enlightenment Thinker - Montesquieu
- French Revolution (한국어 설명)
- French Revolution in 9 Minutes - youtube
- History of French Revolution - 프랑스 대혁명(만화)
- Maximilien Robespierre - leader of Jacobins(Left Party)
- The French Revolution - The best one-hour history
- The Spirit of Laws - Montesquieu
- 나폴레옹과 박정희의 공통점
- General Topic in History
- History of Information Technology (거의 모든 IT의 역사)
- Japanese History (궁금해서 밤새읽는 일본사)
- Jewish History - A Convenient Hatred: The History of Antisemitism
- Korean Modern History (한국현대사)
- 1996년 종로, 엇갈린 운명의 시작 노무현과 이명박
- 4.19혁명 끝나지 않은 울림
- 5.18 광주사태
- 5.18 광주사태 - [장성민의 시사탱크] 광주 5·18때 북한 특수부대 침투했나?
- 5.18 광주사태 특수부대 개입설
- History of China: Second Sino-Japanese War, Bloody Saturday, Nanking
- 노동법 제정 60년의 평가와 발전과제, 노사정의 역할 - 한국경영자총협회
- 노무현이 만난 링컨
- 러일전쟁 (Russo-Japanese War)
- 영상실록 - 1961년 5.16
- 이명박 어린시절
- 정기훈의 역사이야기 - 제9강 을미사변과 을미개혁
- 청일전쟁 First Sino-Japanese War
- 친일파가 득세하게 된 한국 근대사 정리
- 한국근현대사 흐름특강 메가스터디 김정현 선생님
- Middle East (중동, 이슬람, 유대)
- Renaissance and Middle Ages
- Russian History
- Spanish History
- The Kingfisher Atlas of World History
- Alexander the Great (336 ~ 323 B.C.)
- America - Mayan, Aztec and Inca Civilization
- Ancient India, China, North America
- Ancient War in History
- Ancient World - up to Ancient Greek
- Homer's Odyssey
- Persian Empire - Cyrus, Darius and Xerxes
- Roman Empire
- Roman Empire 2 - Julius Cesar
- The Early Middle Age - Fall of Rome, Britain, Byzantine
- The Middle Age - Islam
- The Story of the World - Volume 3: Early Modern Times
- The Story of the World - Volume 4: The Modern Age
- Who was Series
- Mark Zuckerberg - biography.com
- What was D-Day?
- What was Pearl Harbor?
- What was the Great Depression?
- Who was Abraham Lincoln
- Who was Albert Einstein
- Who was Bill Gates?
- Who was Charles Dickens?
- Who was Charlie Chaplin?
- Who was Dr. Seuss?
- Who was Edgar Allan Poe
- Who was Elvis Presely
- Who was Galileo?
- Who was J.R.R. Tolkien
- Who was Jane Austen?
- Who was Leonardo da Vinci (need to be filled from book)
- Who was Lewis Carroll
- Who was Lewis Carroll?
- Who was Marie Antoinette?
- Who was Martin Luther King Jr.
- Who was Seabiscuit?
- Who was Shakespeare?
- Who was Steve Jobs
- Who was Winston Churchill?
- World War 1 and 2
- Fascism
- Hitler's Museum: The Secret History of Art Theft During World War II 1/2
- The Complete History of World War 2 - Hitler Mussolini - Nazism Fascism - Part 1
- The Nazi hatred of the Jews
- Why Did German Nazis Burn Books In Big Fires?
- World War 1 - Battle of Verdun
- World War 1 for Kids
- 김누리 교수 (전체주의자들을 양성하는 교육)
- 왜 인간무리는 괴물이 되는가 - 한나아렌트:전체주의의 기원
- 제1차 세계대전 원인과 경과 그리고 종전의 결과는..?
- 제2차 세계 대전
- 제2차 세계대전 원인과 히틀러와 그리고 독일의 패망
- 토쿄 대공습 (알펀 tv)
- 한나 아렌트 - 전체주의의 기원 (The Origin of Totalitarianism)
- 한나 아렌트의 관점 (Hannah Arent)
- 고종훈 한국사
- 빡공시대 TV
- [8-3]이슬람 세계의 형성과 발전
- [8-4]유럽세계의 발전과 크리스트교 문화 (중세시대)
- [8-5]십자군전쟁
- [9-3]셀주크튀르크 - 서아시아
- [9-4]무굴제국 - 인도의 역사
- [9-5]르네상스,종교개혁,신항로개척,절대왕정
- 중3역사[3-1](2)6.25전쟁
- 중3역사2[1-1](1)흥선대원군의 개혁정치 및 통상수교거부 정책
- 중3역사2[1-2](1)갑신정변 및 동학농민 운동
- 중3역사2[1-2](2)삼국간섭 및 독립협회와 대한제국
- 중3역사2[1-3](1)일제의 국권침탈
- 중3역사2[1-3](2)국권 수호 운동
- 중3역사2[1-4](1)근대 문물의 수용과 사회 및 문화의 변
- 중3역사2[2-1](1)무단 통치
- 중3역사2[2-1](2)3.1운동 및 임시정부
- 중3역사2[2-2](1)문화 통치
- 중3역사2[2-2](2)국내외 민족 운동
- 중3역사2[2-3](1)민족말살 통치
- 중3역사2[2-3](2)1930~1940년대 민족운동
- 중3역사2[2-3]1930~1940년대 민족운동(2)
- 중3역사2[3-1](1)대한민국 수립#1
- 중3역사2[3-1](1)대한민국 수립#2
- 중3역사2[3-2](1)4 19혁명
- 중3역사2[3-2](2)전두환 정부와 민주주의 발전과정#1
- 중3역사2[3-2](2)전두환 정부와 민주주의 발전과정#2
- 중3역사2[4-1]시민혁명과 산업혁명(1)
- 중3역사2[4-2](1)프랑스혁명(2021교육과정)
- 중3역사2[4-2]자유주의와 민족주의의 확산(2)
- 중3역사2[4-2]프랑스혁명(1)
- 중3역사2[4-3](3)라틴아메리카의 독립
- 중3역사2[4-3]미국혁명, 남북전쟁과 러시아의 근대화
- 중3역사2[6-1](1)제1차 세계대전
- 중3역사2[6-1](2)러시아혁명
- 중3역사2[6-1](3)베르사유체제
- 지중해 세계의 통일 - 로마
- 지중해 세계의 통일 - 마케도니아~알렉산드로스
- 지중해 세계의 통일-그리스
- 설민석의 영화로 본 한국역사
- 정기훈의 한눈에 보이는 대한민국 근현대사
- 서재필 (Philip Jason) - 긍정적 그리고 부정적 측면
- 제01강 한국사 시대구분과 근현대사 개요 full [정기훈의 역사이야기]
- 제02강 흥선대원군의 대외정책 full [정기훈의 역사이야기]
- 제03강 흥선대원군의 대내정책 full [정기훈의 역사이야기]
- 제04강 일본과의 통상조약 Full [정기훈 한국사 근현대사]
- 제05강 서양과의 통상조약-임오군란 Full [정기훈 한국사 근현대사]
- 제06강 서양과의 통상조약-갑신정변
- 제07강 동학농민전쟁과 갑오개혁 1
- 제08강 동학농민전쟁과 갑오개혁 2
- 제09강 을미사변과 을미개혁
- 제10강 독립협회와 광무개혁 (서재필)
- 중국 역사 (Chinese History)
- [중국史#2] 중국은 하루 아침에 이뤄지지 않았다 ② - 당나라부터
- [중국地#통합본] 중국 지도 30분 안에 아는척하기
- Documentary: China A Century of Revolution 1949 - 1976
- The Chinese Revolution of 1911
- The Tragedy of Chinese Revolution
- 강희제 (Yongzheng Emperor 청나라)
- 궁금해서 밤새읽는 중국사
- 궁금해서 밤새읽는 중국사 2 - 명, 청, 근대화
- 로빈의 역사기록 - 몽골제국 & 원나라의 역사 한번에 다보기
- 로빈의 역사기록 - 위진남북조시대&수나라의 통일 한번에 다보기
- 로빈의 역사기록 - 중국의 역사 한번에 다보기
- 중국 왕조사 - 전국시대(戰國時代) 이야기
- 중국 왕조사 - 주나라
- 중국 왕조사. 춘추시대(春秋時代) 이야기
- 중국의 근대화 (빡공시대)
- 최진기의 다시 보는 중국 : 중국 근현대사 (2018)
- 한국 근.현대사
- 한국역사
- 갑신정변 - 급진개화파 김옥균 주도, 청나라개입해서 실패
- 강화도 조약
- 대동법
- 도정 권상호의 서예세상
- 독립협회 - 청나라부터의 독립, 서재필주도, 독립신문, 고종이 해산
- 동학농민운동 - 인내천사상 동학, 조선의 신학자 최제우, 천도교 최시형
- 마테오리치(Matteo Rich) maps
- 병인박해
- 병자호란때 박스 사고 Anchoring Effect
- 사도세자
- 삼전도의 굴욕, 남한산성, 인조
- 서예이야기 (calligraphy)
- 안동김씨, 세도정치
- 운산금광 - 평안북도, 미국의 약탈
- 을미사변 - 명성황후 시해 (정기훈 강의)
- 이순신 - 난중일기
- 이순신을 만든 사람들
- 정약용
- 정조 - 수원능행도
- 질문조선시대 왕들의 순서와 업적 (27대) - '조'와 '종'
- 탕평책 - 공평한 당파 인용, 탕평채와 관련
- 한국에 김씨가 많은 이유
- 홍경래의 난
- 흥선대원군
- Humanity Classsics
- Karl Barth
- Evangelical Theology - An Introduction
- Prayer
- Sermons and Short Papers
- The Great Passion - An Introduction to Karl Barth's Theology - Eberhard Busch
- The Humanity of God
- 김명용 교수의 논문, 글, 그리고 영상
- 개혁교회신학의 역사적 조명 - 김명용
- 개혁신앙의 전통과 오늘의 고백신앙 - 정책포럼 (2009/06/16)
- 개혁신앙의 전통과 오늘의 고백신앙에 대한 논찬 - 김명용교수 (2009/06/16)
- 개혁신앙의 전통과 오늘의 고백신앙에 대한 논평 - 장동민교수 (2009/06/16)
- 김명용 총장 장신대 채플 설교 (2013-08-27)
- 뉴욕교협, 이단대책 세미나 “요한계시록을 바로보자” - 김명용
- 바른 교회 되려면 신학자 존경해야 - 김명용
- 예정론에 대한 바른 신학적 이해 - 김명용
- 장신대 신학의 정체성에 대해 말한다 - 김명용 교수
- 칼빈의 신앙유산과 한국 교회의 목회적 전망 - 이재천목사 (2009/06/16)
- 이 시대의 바른 기독교 사상 - 김명용
- 칼 바르트신학입문 강의록 - 김명용
- 칼바르트 관련 논문들
- 칼바르트 관련 블로그 사이트
- Karl Barth (1886 - 1968) from Wikipedia
- Karl Barth on Genesis
- The Babylonian Myth와 성경의 창조신화
- 교만에 대한 신학 (Theology of pride)
- 단군신화
- 어거스틴과 바르트의 시간이해 - 김경재 (한신대교수)
- 에누마 엘리쉬와 창조 이야기
- 칼 라너의 익명의 그리스도인
- 칼 바르트, 그는 왜 한국교회에서 ‘논쟁적’ 신학자인가
- 칼 바르트의 교회교의학 (성서관) - 개혁신학연구소
- 칼 바르트의 성경관 비판 - 김향주 교수 / 조직신학(대신대 신학대학원)
- 칼바르트의 신학적 해석학
- 하르낙과 바르트의 논쟁
- 칼바르트의 신학 (The Theology of Karl Barth) - 김명용 지음
- Korean Books (한국책)
- 지적대화를 위한 넓고 얕은 지식 2 - 채사장 (진리, 철학, 과학, 예술, 종교, 신비)
- 가장 공적인 연애사 (오후 지음)
- 고미숙
- 공간이 만든 공간 - 유현준
- 국가 (The Republic)
- 김상근 - 군주의 거울 (The Education of Cyrus)
- 김상근 - 마키아벨리 (세상에서 가장 위험한 현자)
- 김상근 교수의 인문학 강의
- [김상근] 의 르네상스 인문학 산책] 1강 - 인문학의 고향 그리스를 가다
- [김상근의 르네상스 인문학 산책] 10강 - 로마제국은 왜 쇠퇴했는가
- [김상근의 르네상스 인문학 산책] 2강 - 호메로스의 세계 (Iliiad)
- [김상근의 르네상스 인문학 산책] 2강 - 호메로스의 세계 (Odyssey)
- [김상근의 르네상스 인문학 산책] 4강 - 펠로폰네소스의 전쟁사
- [김상근의 르네상스 인문학 산책] 5강 - 소크라테스와 플라톤
- [김상근의 르네상스 인문학 산책] 6강 - 크세노폰과 키루스
- [김상근의 르네상스 인문학 산책] 7강 - 플루타르코스의 영웅전
- [김상근의 르네상스 인문학 산책] 8강 - 로마 공화정과 키케로
- [김상근의 르네상스 인문학 산책] 9강 - 로마제국과 어거스틴
- [신과 인간의 경계] 1강 - 그리스도교와 이집트 문명 (김상근)
- [신과 인간의 경계] 2강 - 동서문명의 만남 (김상근)
- [신과 인간의 경계] 3강 - 그리스도교와 반유대주의의 역사 (김상근)
- [신과 인간의 경계] 4강 - 세계 지도의 역사와 한반도의 지리적 발견 (김상근)
- [신과 인간의 경계] 5강 - 한국 그리스도교의 기원 (김상근)
- 1강 개신교적 의식의 탄생(김상근) - 미완의 기획 종교개혁
- 김상근 : 인문학, 어떻게 시작됐는가? 무엇을 할 것인가?
- 김상근의 르네상스 인문학 산책] 3강 - 헤로도토스의 역사
- 단테, 그분이 알고 싶다 - 김상근 교수
- 스무 살, 서양 고전을 만나다 - 인문학이 추구하는 가치(김상근 교수)
- 예루살렘과 아테네가 무슨 상관이 있는가?(김상근 교수)
- 인문학(Humanities)과 인본주의(Humanism)의 차이
- 천병희 선생의 "펠로포네스 전쟁사" 서문
- 나의 한국현대사 - 유시민
- 내 아이를 위한 인문학 교육법
- 논어
- 논어로 배우는 한자
- 눈 떠보니 선진국 - 박태웅
- 동양철학사를 보다
- 로마제국 쇠망사 (Decline and Fall of Roman Empire)
- 리딩으로 리드하라(이지성) - 인문고전 독서법
- 미리보는 서양 문학, 사상 베스트 30
- 미움받을 용기
- 사진과 그림으로 보는 한국 현대사 - 서중석
- 세상에서 가장 쉬운 상대성이론 - 박홍균
- 스토리가 스펙을 이긴다 - 김정태
- 시민의 교양 - 채사장
- 이야기 교회사
- 이야기 논어 - 기독교와 유교, 그리스철학과 유교
- 이외수
- 이원복 교수의 와인의 세계
- 정선 사서 - 논어, 맹자, 대학, 중용
- 지대넓얕 - PodCast
- 지적대화를 위한 넓고 얕은 지식 1 - 채사장 (역사, 경제, 정치, 사회, 윤리 편)
- 청소년을 위한 서양 문학사
- 청소년을 위한 서양수학사
- 청소년을 위한 서양음악사
- 청소년을 위한 지금 시작하는 인문학 1 (가로읽기) - 주현성
- 청소년을 위한 지금 시작하는 인문학 2 (세로읽기) - 동양철학
- 청소년을 위한 한국 철학사
- 청소년을 위한 한국근현대사
- 최인철 - 프레임 (나를 바꾸는 심리학의 지혜)
- 최진기 - 교실밖 인문학
- 최진기 오마이스쿨 대표
- 크리스찬이면 꼭 알아야할 이야기 교회사
- 플라톤 아카데미 - [8대 고전읽기]
- 하룻밤에 읽는 한국사
- 고구려 - 을지문덕, 연개소문, 신라통일, 계백장군, 황산벌전투
- 고려시대 왕건, 거란침입, 서희의 강동6주, 묘청의 난
- 고려청자, 금속활자, 삼국사기, 삼별초
- 고인돌 - 2만게 정도 남한에만
- 광개토대왕 - 평양천도
- 단군신화
- 단재 신채호
- 백강전투(김용운 교수) - 백제와 나당연합군, 기마민족 후예설
- 백제, 신라(이차돈의 순교). 선덕여왕
- 삼국의 건국신화
- 오 한강 1 - 허영만
- 오 한강 2 - 5.26전쟁과 강토의 시련, 애치슨라인
- 오 한강 33 - 혼돈의 전후시대, 조봉암
- 전라도 차별의 역사, 그리고 지역감정의 역사
- 조광조,
- 조선시대, 이성계, 세종대왕, 수양대군, 연산군(흥청망청)
- 크로체 - 모든 역사는 현재의 역사이다.
- 통일신라와 발해, 원효대사, 장보고, 골품제, 궁예몰락
- Lynda.com
- Drawing Vector Graphics
- Godot Platform Jumper Tutorial - HeartBeast
- Platformer Game Tutorial P1
- Platformer Game Tutorial P2 - Tiles and Animated Sprites
- Platformer Game Tutorial P3 - Smooth Character Movement
- Platformer Game Tutorial P4 - Moving Between Levels
- Platformer Game Tutorial P5 - Autotiles
- Platformer Game Tutorial P6 - Parallax Background
- Platformer Game Tutorial P7 - Menu UI and Signals
- Home Studio
- 4K Projectors
- Acoustic Panel
- Amplifier
- Dynaudio Professional M3XE, Core47, LYD48
- Dynaudio Wall Speakers (Dynaudio Custom Studio series)
- Dyneaudio Contour 30
- How to Set Up a PA System for a Band
- How to Set Up a PA System for Solo/Duo Acts
- On-Wall Loudspeakers (Focal French Speaker)
- Paul Davids - Home Studio Tour
- Illustrator
- Illustrator CC 2018 Essential Training
- Kids Can Code - Godot 101
- Dodge the Creep Tutorial : Your First Game
- Dodge the Creep Tutorial (다시만들기)
- Godot 101 - Part 10: RayCasts (and Jumping)
- Godot 101 - Part 11: Animated Sprites
- Godot 101 - Part 12: Camera and Scrolling Background
- Godot 101 - Part 14: Intro to RigidBody2D
- Godot 101 - Part 3: Scripting
- Godot 101 - Part 4: Instancing Scenes (Shortcuts GDscript Editor)
- Godot 101 - Part 5: Player-controlled Sprite
- Godot 101 - Part 6: Area-based Collisions
- Godot 101 - Part 7: Using Signals (custom event handler)
- Godot 101 - Part 8: Tweens and Timers
- Godot 101 - Part 9: Arcade Physics (KinematicBody2D) - Old version
- Godot 2.1 to 3.0 Gotchas!
- Godot 3.0 - Know Your Nodes: Particles2D
- Godot 3.0: Rigid Bodies (Angry Bird)
- Godot Engine - Know Your Nodes: Tilemap (part 1)
- Godot Short Keys
- Make a Space Shooter Game in Godot
- RayCast2D
- Space Rocks! Godot Game Tutorial Part 1 [eBook]
- Kids Can Code - Platformer
- Platformer Part 1: Setting Up
- Platformer Part 10: Character Animation (part 1)
- Platformer Part 11: Character Animation (part 2)
- Platformer Part 12: Platform Graphics
- Platformer Part 13: Improved Jumping
- Platformer Part 14: Sound and Music
- Platformer Part 15: Powerups
- Platformer Part 16: Enemies
- Platformer Part 17: Using Collision Masks, Pixel Perfect Collision
- Platformer Part 18: Scrolling Background
- Platformer Part 2: Player Movement - Equation of Motion (운동법칙)
- Platformer Part 3: Gravity and Platforms
- Platformer Part 4: Jumping
- Platformer Part 5: Scrolling the Window
- Platformer Part 6: Game Over and Score
- Platformer Part 7: Splash & End Screens
- Platformer Part 8: Saving High Score
- Platformer Part 9: Using Spritesheets
- Kids Can Code - Shump
- Getting Started with Pygame - Game Assets
- Shmup Part 10: Explosions, and Auto shoot
- Shmup Part 11: Player Lives
- Shmup Part 12: Powerups
- Shmup Part 14: Game Over
- Shmup Part 2: Enemy Sprites
- Shmup Part 3: Collisions (and Bullets!)
- Shmup Part 4: Adding Graphics
- Shmup Part 5: Improved Collisions
- Shmup Part 6: Sprite Animation (difficult)
- Shmup Part 7: Score (and Drawing Text)
- Shmup Part 8: Sound and Music
- Shmup Part 9: Shields
- Shump Part 1: Player Sprite and Controls
- Working with Sprites
- Kids Can Code - Tile-based game
- Tile-based game Part 1: Setting up
- Tile-based game Part 2: Collisions and Tilemap
- Tile-based game Part 3: Smooth Movement (Difficult)
- Tile-based game Part 4: Scrolling Map / Camera (Difficult)
- Tile-based game Part 5: Player Graphics
- Tile-based game Part 6: Rotating Player Sprite (Difficult)
- Tile-based game Part 7: Mobs
- Tile-based game Part 8: Mob Movement
- Tile-based game Part 9: Basic Shooting
- Math
- Program Arcade Games: With Python and Pygame
- Animating Snow, 3D Blender Game Engine
- Bitmap graphic, Sound
- Bouncing Rectangle
- Controlling an object with keyboard
- Game class structure
- Graphic and Pygame Library - Window, Drawing
- Guessing Game (Loop)
- If statement
- More Games
- python-forum.io - Basic Animation
- python-forum.io - Enemy AI and collision
- python-forum.io - Game State
- simple encryption
- Sprite and Collision Detection
- Stick Figure Man - Mouse position
- Trigonometry to Animate Bounces
- Wing IDE and Custom Calculator
- Python - Pygame Race Car
- 2. Python Basics
- Atom Package
- Atom Short Keys
- Game Assets and Images
- How make Atom work with python3 instead of default python
- Installing Python on Mac
- Pygame development
- Pygame Race Car 1
- Pygame Race Car 2 - moving an image
- Pygame Race Car 3 - Display text
- Python Related Tips
- Space Shooter DEMO
- Space Shooter tutorial
- Working with Dates and Time
- Working with Files
- Python - Real World Programming
- Teaching Methods and Skills
- Writing a Research Paper
- Drawing Vector Graphics
- Medical Knowledge
- ADHD(Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder)
- Delivered from Distraction - Edward M. Hallowell
- General Family Practice
- Screen Addiction
- Tech Diet for your child and teen
- 건강장수 120세를 위한 몸과 마음 관리 (염용운)
- 과민성 대장 증후군 (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
- 동의보감
- 이상곤의 낮은 한의학
- 저속노화 (Slow Aging)
- 젊음은 나이가 아니라 호르몬이 만든다
- 한방관련 기본상식
- Movie and Music
- Bible Related Movies for My Kids
- Bible Studies with My Kids
- Books for my kids
- Christian's Favorite Music
- Classical Guitar Cover - 유명한 음악
- Ana Vidovic plays Asturias by Isaac Albéniz
- Bach´s Cello Suite No. 1
- Cavatina - Ana Vidovic
- Fernando Sor - Andante n.13, op.35, Uros Baric
- Fernando Sor - Andantino Op 32 No. 01
- Fernando Sor - etude no. 11 op.6 Allegro moderato
- Fernando Sor - Etude No. 22, Op. 35: Allegro
- Fernando Sor - introduction and variations on a theme by Mozart
- Fernando Sor - n.17 (Moderato), op.35, Uros Baric
- Fernando Sor - Op 6 No 11 (Etude 17)
- Francisco Tarrega - Adelita - Tavi Jinariu
- Francisco Tarrega - Capricho Arabe - Tatyana Ryzhkova
- Francisco Tarrega - La Paloma
- Francisco Tarrega - Recuerdos de la Alhambra - Ana Vidovic
- Franciso Tarrega - Estudio E-minor
- J. S. Bach - Air on G String
- J. S. Bach, Prelude BWV 998 by Tatyana Ryzhkova
- J. S. Bach: Preludium in C from The Well-Tempered Clavier BWV 846
- J.S. Bach - Air on G string, BWV 1068
- J.S. Bach - Allegro Assai from BWV 1005
- J.S. Bach - Allegro from Violin Sonata no. 2 BWV 1003
- J.S. Bach - Bist du bei mir (BWV 508)
- J.S. Bach: Four Lute Suites Gavotte en Rondeau No. 4 in E Major, BWV 1006a
- Classical Guitar Lesson
- A Time For Us (Romeo and Juliet) Michael Marc
- Ask Tatyana - Warm up Special
- Bach Chorale Prelude BWV645 - Per-Olov Kindgren
- Bach WTK Preludium 1 BWV846
- Cavatina - Joshua Rogers (Lesson)
- Cavatina as John Williams
- Cinema Paradiso
- Fernando Sor - Study In B-minor
- Fernando Sor: Study Bb Major Op. 29 n. 13
- Hallelujah (Classical Guitar) performed by Per-Olov Kindgren
- introduction and variations on a Theme by Mozart (연주)
- Lágrima - Francisco Tarrega
- Maximo Diego Pujol - Verde Alma
- Once Upon a Time in America - Deborah's Theme
- Recuerdos de la Alhambra
- Romance
- Sunflower - Henry Mancini
- The Umbrellas of Cherbourg(쉘브르의 우산)
- Tremolo Exercises - 3, 4, & 5 fingers
- Vivaldi Largo Winter - Per-Olov Kindgren
- 클래식칼 기타 레슨 (Seyoung Guitar)
- Classical Guitar Lessons from Yuri
- Allegretto - F. Carulli
- Allegro - Mauro Giuliani
- Allegro by S. Suzuki
- Antonio Lauro - Valse Criollo No. 3
- Bach - BWV 995 Gavotte I & II (from Suite No. 6 in D for Cello)
- Bach Cello Suite 1 - Allemande
- Bach Cello Suite 1 - Courante
- Bach Cello Suite 1 - Gigue
- Bach Cello Suite 1 - Minuet I & II
- Bach Cello Suite 1 - Prelude BWV 1007
- Bach Cello Suite 1 - Sarabande
- Canco del Lladre
- Capricho Arabe - Tárrega
- Cavatina - Stanly Myer
- Danza Brasilera
- Endecha y Oremus - Francisco Tarrega
- Etude No. 1 by Heitor Villa Lobos
- Etude Op. 60, No. 19 - Fernando Sor
- Etude Op. 60, No. 7 - Matteo Carcassi (1792 - 1853)
- Evocación - Jose Luis Merlin
- Ferdinando Carulli: Concerto in A major Allegro
- Fernando Carulli - 29 Practices
- Fernando Sor - Estudio 17 (Op. 6 No. 11)
- Fernando Sor - study in b minor
- Fernando sor Op 35. No 17.
- Fernando Sor op. 60, No. 5
- Fernando sor study op. 60 no 22
- Gabriels Oboe arranged by Carlo Marchione
- Giuliani 120 right hand studies
- How to Change Strings on Classical Guitar with a 12 Hole Bridge
- Improve Your Musical Rhythm w/ Metronome Exercises
- J.S. Bach - Bist du bei mir (BWV 508)
- J.S. Bach - Largo from Violin Sonata BWV 1005
- J.S. Bach - Sonata for Violin Solo No. 2 (Andante)
- Jesus, Joy of Man's Desiring
- Julia Florida - Agustin Barrios Mangore
- Konstantin Vassiliev - Cinderella
- Lagrima - Francisco Tarrega
- Laputa: Castle in the Sky | Carrying You | Joe Hisaishi
- Largo and Rondo - Ferdinando Carulli
- Leo Brouwer Etudes Simples no. 6
- Long, Long Ago by T.H. Bayly
- Malagueña - Francisco Tarrega
- Maria - Francisco Tarrega
- Maria Luisa - Julio Salvador Sagreras
- Matteo Carcassi - 25 Etudes op. 60
- Matteo Carcassi - Etude, Op. 60, No. 3
- Matteo Carcassi - Hermina Polka
- Matteo Carcassi Op.59 No.1 Andante Grazioso
- Oblivion
- Prelude in C Minor - Agustin Barrios Mangore
- Prelude no 1 by Heitor Villa-Lobos
- Prelude No. 3 by Heitor Villa Lobos
- Prelude, Fuge and Allegro BWV 998
- Preludio de Adios - Alfonso Montes
- Recuerdos de la Alhambra
- Romanza d'Espagna (로망스)
- Russian Waltz - Lawrence Ferrara
- Scale
- Sheep May Safely Graze - J. S. Bach
- Siciliana by M. Carcassi
- Un Dia de Noviembre - Leo Brouwer
- Vals Jose Ferrer
- Variations on a Theme of Mozart by Fernando Sor
- Vivaldi - Concerto in D Major RV 93 (Largo)
- Vivaldi - Largo from Winter, The Four SSeason
- Waltz No.1, Bartolome Calatayud (1882 - 1973)
- Yesterday - by Toru Takemitsu
- Yuri Liberzon
- Yuri's teachers - Manuel Barrueco
- Zapateado - Regino Sainz de la Maza
- Classical Movies
- Classical Music - Beethoven
- Dance and Hip Hop
- Guitar Covers - Pop Songs
- Dust in the wind (연주)
- Falling Slowly - Glen Hansard & Lisa Hannigan
- Freddie Mercury and Michael Jackson - There Must Be More to Life Than This
- Stairway to Heaven - Acoustic Cover by Junik
- Stairway to Heaven - Guitar Solo
- Stairway To Heaven - Igor Presnyakov
- Tears in Heaven (Boyce Avenue acoustic cover)
- Guitar Lesson Videos (영어)
- Vincent - Don Mclean
- When I was Your Man - Bruno Mars
- All Alone (Naturally) - rk
- Always on my mind
- Can't Take My Eyes Off Of You (정아로)
- Desperado - Eagles
- Desperado - Egles (Rolf Maibaum)
- End of the Road - Boys 2 Men
- Falling Slowly
- Gravity - Sara Bareilles
- Hallelujah - Leonard Cohen
- Hotel California classical guitar
- How Deep Is Your Love (정아로)
- I could sing of your love forever
- I Don't Know How to Love Him
- I don't wanna miss a thing (Acoustic)
- I want to break free
- Imagine - John Lennon
- J.S.Bach - Prelude in C Major
- just when i needed you most - Randy Vanwarmer (1979)
- Let It Be - Beatles
- Love of My Life - Queen
- Love of My Life - Queen
- Man in the mirror - Michael Jackson
- More Than Words - Extreme
- Now and Forever
- Now and Forever - Richard Marx (네이버 카페)
- Officially Missing You - Jayesslee
- One Last Cry
- One Last Cry - Brian Mcnight
- Perfect - Ed Sheeran
- Seasons of Love
- Somewhere Over The Rainbow - Israel Kamakawiwo'ole
- Stairway to Heaven - Led Zeppelin
- Tears in Heaven - Eric Clipton
- Tears In Heaven - Eric Clipton
- The Boxer - Simon and Garfunkel
- There is none like you - Lenny Leblanc
- There must be more to life than this
- Today - John Denver
- Vincent
- What's Up - 4 Non Blondes
- When we were young cover
- Wonderful Tonight 통기타
- Yesterday - Beatles
- You are God alone
- 기타 연주 실력 늘리려면 (기타리스트 임선호)
- 오브리닷컴 - 퍼커시부 주법
- Guitar 악보 (가요)
- 가리워진길 (볼빨간사춘기)
- 갈수없는 나라 (해바라기)
- 거리에서 - 김광석
- 겨울바다 (푸른하늘)
- 그대 (이문세)
- 그대 내게 다시
- 그대 내품에 (유재하)
- 그대와 영원히 (유재하 작곡)
- 그런 사람 또 없습니다
- 꿈결같은 세상
- 나의 봄은(나의 해방일지 OST)
- 나의 옛날이야기 (혜원 진)
- 내 사람이여
- 내 사랑 내 곁에 (신지훈)
- 내일(미생 - 한희정)
- 내일이 찾아오면
- 라구요 (강산에)
- 매일 그대와 (소진)
- 모든 날 모든 순간
- 보통의 하루(정승환)
- 비와당신 (이무진)
- 비처럼 음악처럼
- 사랑 그대로의 사랑 (유영석) - 피아노
- 사랑이 지나가면 (예빛)
- 사랑하기 때문에 - 유재하
- 소녀(정세운)
- 씨스루(권진아)
- 어떻게 이별까지 사랑하겠어 - 악동뮤지션
- 얼굴 - 김건모
- 엘렐릴리 (강산에)
- 여전히 아름다운지 - 김연우
- 옛사랑 (혜원 진)
- 오랜 날 오랜 밤 (악동 뮤지션)
- 일종의 고백
- 일종의 고백 (Female Ver.)
- 잊어야한다는 마음으로 - 김광석
- 자랑 - 곽진언
- 제주도의 푸른밤
- 주저하는 연인들을 위해 - 잔나비
- 축복합니다 (들국화)
- 편지 (김광진)
- 함께 - 박광현, 김건모
- Harmonica
- History Lessons Through Movies
- Hymn Favorite
- Logic Pro
- Lyrics
- Movies about dating and love
- Movies for My Kids
- 7 Days in Tibet
- A Walk to Remember Trailer
- Billiy Elliot
- Good Speech in movies - Patch Adams last scene
- Good Speech in movies - Scent of Woman (Al Pachino)
- Ice Castle
- Il Postino - Love is metapho
- It's A Wonderful Life
- Lorenzo's Oil (1992)
- Miyazaki - Howl's Moving Castle
- One flew over the cuckoo's nest
- Oscar Award Winning Movies
- Splender in the grass (1961) - 초원의 빛
- The Empire of the Sun (1987)
- The Last Concert (1976)
- The Mission (1986)
- The Natural
- The Shawshank Redemption - Quotes
- 장미의 이름 (The Name of Rose) - Umberto Eco
- Music Videos
- Musical Music
- Musicians
- Johann Sebastian Bach - Air on the G String
- Antonio Vivaldi - The Four Seasons
- Dvorak - Humoresque
- Franz Schubert - Trout Quintet 4th Movement
- Frédéric Chopin - Nocturne no. 20 in C-sharp minor
- George Frideric Handel - Water Music
- Ludwig van Beethoven - Emperor, 5th Piano E-flat major, Op. 73
- Tchaikovsky - Swan Lake
- Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart - Eine kleine Nachtmusik
- 소향
- Original Sound Track
- Breakfast at Tiffany - Moon River
- Cinema Paradiso - Love Theme Violin with Orchestra
- Cinema Paradiso - Waiting Outside
- Life is Beautiful
- Love Story - Snow Frolic and Love Theme
- Malena (Ennio Morricone)
- Once Upon a Time in America
- Once Upon a Time in the West - dell'art
- Romeo and Juliet - A Time for Us
- The Godfather – The Danish National Symphony Orchestra
- The Pianist (2002)
- White Nights - Mikhail Baryshnikov dance in theater
- Painters
- Piano Tutorial
- Song Writing and Composition
- Studio Recording
- 5 Easy Steps to Mixing Vocals Like a Pro!
- Acoustic Guitar Record
- Audio Mixing Bootcamp with Bobby Owsinski
- Audio Recording Techniques with Bobby Owsinski
- Foundations of Audio: EQ and Filters with Brian Lee White
- GarageBand Essential Training with Garrick Chow
- How To Record VOCALS With The APOLLO TWIN + UAD
- How to Use The Apollo UAD for Vocals
- iMovie 11 Essential Training with Garrick Chow
- Lighting for YouTube Videos
- Logic Pro - Drum
- Setting up UA Interfaces for Logic Pro X on Mac OSX
- Studio Lighting (Photograph)
- Studio Lighting For Beginners
- Vocabulary related to Recording Technique
- VBS 2013 - Kingdom Rock
- Vocal Training
- [보컬트레이닝] 남성과 여성의 보컬의 차이
- [보컬트레이닝] 초기두성하는 방법
- AmaZane Channel
- Gentle Singing Warm Up - Baritone
- 고음, 두성 Head voice 발성 - 1편
- 고음, 두성강좌 - 허밍 2, 3단계 트레이닝 - 노래 적용
- 기초발성법:01강/우리 몸이 이해하는 소리의 구조1 voice color
- 기초발성법:02강/우리 몸이 이해하는 소리의 구조2 (나의 소리)
- 기초발성법:03강/우리 몸이 이해하는 소리의 구조3 (분석법 연구)
- 기초발성법:04강/복식 호흡과 기초발성 1
- 기초발성법:05강/복식 호흡과 기초발성 2
- 기초발성법:06강/복식 호흡과 기초발성 3
- 기초발성법:07강/말하듯이 노래하기, 노래하듯이 말하기
- 기초발성법:08강/
- 기초발성법:09강/비강 사용하여 목을 상하지 않게 노래하기말하기
- 기초발성법:10강/발음하며 호흡 해보기
- 기초발성법:11강/
- 기초발성법:12강/Bouns 연구 분석곡분석
- 기초발성법:13강/입으로 익히는 리듬A new song
- 기초발성법:14강/꾸밈음분석과 가창실습,training
- 보컬트레이너 한의 5분 발성 마스터!
- 크로스 김혁건 보컬강좌 노래잘부르는방법 1화 호흡법
- 크로스 김혁건 보컬강좌 노래잘부르는방법 2화 두성법
- 화성학 무료강의 - 박하얀 - 다른 조에서 빌려온 3화음 [뮤직필드]
- Watch list
- 네이버카페 통기타노래 악보
- 서부영화 리스트
- 이근성 클래식 기타 소품집
- 클래식 기타 명곡집 1
- 클래식 기타 명곡집 2
- Adelita - Franciso Tarrega
- Andante Fernando Sor op. 31, no. 4
- Andantino in E major, Op. 32-1, by Fernando Sor
- Barcarolle(뱃노래) - Napoleon Coste
- Españoleta - Gaspar Sanz
- Estudio En E Minor - Francisco Tarrega
- Etude V (Op. 35, No. 22) 월광 - Fernando Sor
- Feste Lariane - L. Mozzani
- Kleine Romanze - Luise Walker
- La Danse des Naiades Ferrer - J. Ferrer
- Lágrima - Francisco TÁRREGA
- Nocturne ops.9 No. 2 - Chopin
- Nocturno - C. Henze
- Pas du Cygne (백조의 걸음) - F. A. Marsaglla
- Pastorale - Carcassi
- Pavanas - Gaspar Sanz
- Prelude, Op. 28, No. 7 - F. Chopin
- Raindrops - G.C.Lindsey
- Romanze, Op.13, Adagio in E minor - J. K. Mertz
- Valse Andantino - Antonio Cano
- Waltz in E major, Op. 32-2, by Fernando Sor
- Parenting
- Awakened Family - Shefali Tsabary
- 10. Myth#7: Parents need to be in control
- 11. Raising the real child
- 12. What's really behind our reactions
- 13. Transforming fear into consciousness
- 14. From expectation to engagement
- 15. From mindless reaction to mindful presence
- 16. From chaos to stillness
- 17. From role to no-role
- 18. From emotion to feeling
- 2. How the culture sets up parents to fail
- 3. The invisible triggers of our reactivity
- 4. Myth#1: Parenting is about the child
- 5. Myth#2: A successful child is ahead of the curve
- 6. Myth#3: There are good children and bad children
- 7. Myth#4: Good parents are naturals
- 8. Myth#5: A good parent is a loving one
- 9. Myth#6: Parenting is about raising a happy child
- Learning a New Way
- General
- Grace Based Parenting - Tim Kimmel
- How and When to Tell Your Kids About Sex
- How to raise an Adult - Julie Lythcott-Haims
- How to Talk so Kids will Listen & Listen so Kids will Talk
- Out of Control - Why discipling your child doesn't work - Shefali Tsabary
- 10. Abandon the idea of perfection
- 1. Why discipline doesn't work?
- 11. Strong child lives here
- 12. It's not about you
- 13. Learned to read your child's cues
- 14. What it means to honor your child
- 15. Is what you are asking fair?
- 16. How to stay sane as your child goes through phases
- 17. Tricking children is tricky business
- 18. What to do when your child shuts you out
- 19. The rule about rules
- 2. A World that majors in controls
- 20. How to respond to a teen who rebels
- 21. Avoid homework battle
- 22. Why do children bully?
- 23. The challenge of sibling rivalry and children who can't get along with other children
- 24. When you spare the rod, you don't spoil your child
- 25. Hidden reason why we discipline
- 26. The power of connection
- 3. Is it really for your child's own good?
- 4. Let consequences do their job
- 5. How rescuing our children teaches irresponsibility
- 6. How to make your child's limit clear
- 7. Your children are here to challenge your integrity
- 8. How to say Yes or No effectively
- 9. You are not a moviemaker (라쟈냐)
- Parenting with Love and Logic (2006) - Foster Cline, Jim Fay
- The 5 Love Languages of Children - Gary Chapman & Ross Campbell
- The Big Disconnect: Protecting Childhood and Family Relationships in the Digital Age
- The Conscious Parent - DrShefali Tsabary
- The Formula - Ronald F. Ferguson
- The Self-Driven Child: The Science and Sense of Giving Your Kids More Control Over Their Lives
- The Whole-Brain Child - Daniel J. Siegel
- ** Wellness Wheel
- 1. Survive and Thrive
- 2. Two Brains are Better than One - Integrating the Left and Right
- 3. Building the Staircase of the Mind - Integrating the Upstairs and Downstairs Brain
- 4. Kill the Butterflies - Integrating Memory for Growth and Healing
- 5. United States of Me
- Chapter 6 - Me-We Connection (Integrating Self with Other)
- www.greatschools.org
- www.skillsyouneed.com
- Awakened Family - Shefali Tsabary
- Paul Tillich
- A Brief Overview of the Life and Writings of Paul Tillich - Daniel J. Peterson
- Biblical Religion and The Search for Ultimate Reality
- Essays and Short Writings
- His Life & Thought Volume 1: Life - Wilhelm & Marion Pauck
- Paul Tillich
- '하나님위에 계신 하나님'의 내재성 - 김형욱 (20세기 신학)
- A Conversation with Dr. Paul Tillich (YouTube)
- Comparison between Tillich's Theology and Traditional Theology
- Lecture Notes T-500 Paul Tillich - Charles W. Allen
- Paul Tillich as Hero: An Interview with Rollo May
- Paul Tillich by Russell Re Manning - St Johns Nottingham
- Paul Tillich Timeline (pdf)
- Paul Tillich’s Gift of Understanding
- Paul Tillich가 전통적인 신학 (traditional theology)과 다른 점들
- Paul Tillich의 신학방법론 - 이삼생 (교원대학 논문집 1986)
- Russell Re Manning about Paul Tillich
- Sermon - You Are Accepted
- The significance of the history of religions for the systematic theologian (1965)
- The Symbolistic Christology of Paul Tillich - H.D. McDonald(1988)
- Tillich for Beginners: Part I
- Tillich for Beginners: Part II
- Tillich관련 비디오
- Ultimate Concern - Tillich in Dialogue by D. Mackenzie Brown
- 실존주의 신학
- 틸리히 관련 질문들, Research Topics, etc
- 틸리히에게 미친 영향들
- 폴 틸리히 - 윤재정 신학자료실
- 폴 틸리히 (Paul Tillich, 1886~1965)
- 폴 틸리히 평가 - from 창조신학연구소
- 폴 틸리히의 상관방법의 신학 - 늘푸른교회
- 폴 틸리히의 신학 - 황민효
- 폴 틸리히의 신학 방법론 - 허호익(한국신학마당)
- 폴 틸리히의 신학에서 본질 실존 그리고 생명의 체계 - 신학논단
- 폴 틸리히의 신학적 해석학 - 임영금 호남신학대 교수
- Perspectives on 19th & 20th Century Protestant Theology
- Perspectives on 19th & 20th Century Protestant Theology
- Systematic Theology (Volume 1)
- The Courage To Be
- The Dynamics of Faith
- Doubt and Faith (믿음과 의심에 관한 이야기, 영희, 철수, 민수)
- Introduction by Marion Pauck
- Symbols of Faith - Religious Symbols
- Symbols of Faith - Symbols and Myth
- Symbols of Faith - The Meaning of Symbols
- Types of Faith - Elements of Faith and Their Dynamics
- Types of Faith - Moral Types of Faith
- Types of Faith - Ontological Types of Faith (거룩, 성례적인것)
- Types of Faith - The Unity of the Types of Faith
- What Faith Is - 1. Faith As Ultimate Concern
- What Faith Is - 2. Faith as a Centered Act
- What Faith Is - 3. The Source of Faith
- What Faith Is - 4. Faith and the Dynamics of the Holy
- What Faith Is - 5. Faith and Doubt
- What Faith Is - Faith and Community
- What Faith Is Not - The Emotionalistic Distortion of the Meaning of Faith
- What Faith Is Not - The Intellectualistic Distortion of the Meaning of Faith
- What Faith Is Not - The Voluntaristic Distortion of the Meaning of Faith
- The Essential Tillich
- The History of Christian Thought
- 1. Introduction - The concept of dogma
- 2. The Preparation for Christianity
- 3. Intertestamental Period
- 4. Apostolic Fathers: Clement. Ignatius.
- 5. The Apologetic Movement - Celsus and Justin Martyr
- 6. Gnosticism and anti-Gnostic Fathers
- Common things that happens through out church history
- Neo-Platonism
- Trends in the Middle Age
- The Interpretation of History
- The Irrelevance and Relevance of the Christian Message
- The New Being
- The Protestant Era
- The Shaking of the Foundations
- Chapter 1: The Shaking of the Foundations (Jeremiah 4:23-30, Isaiah 54:10)
- Chapter 10: The Experience of the Holy (Isaiah 6)
- Chapter 11: The Yoke of Religion (Matthew 11:25 ~ 30)
- Chapter 12: The Meaning of Providence
- Chapter 13: Knowledge Through Love
- Chapter 14: Doing the Truth
- Chapter 15: The Theologian
- Chapter 16: The Witness of the Spirit to the Spirit
- Chapter 17: He Who Is the Christ
- Chapter 18: Waiting
- Chapter 19: You Are Accepted 죄가 더한 곳에 은혜가 더욱 넘쳤나니 (Sin and Grace)
- Chapter 2: We Live in Two Orders (Isaiah 40)
- Chapter 20: Born in a Grave
- Chapter 21: The Destruction of Death
- Chapter 22: Behold, I Am Doing a New Thing
- Chapter 3: The Paradox of the Beatitudes
- Chapter 4: The Two Servants of Jahweh
- Chapter 5: Meditatioin: The Mystery of Time
- Chapter 6: The Escape from God
- Chapter 7: The Depth of Existence
- Chapter 8: On the Transitoriness of Life
- Chapter 9 : About nature
- The Spiritual Situation in Our Technical Society
- Theology of Culture (문화의 신학)
- Tillich by Topics or ideas
- 폴틸리히 관련 자료(Blog or Papers)
- Philosophy
- A Little History of Philosophy - Nigel Warburton
- Aristotle
- 7. The Consolation of philosophy (Boethius)
- David Hume - The Imaginary Watchmaker
- Immanuel Kant
- Jean-Jacques Rousseau - Born Free
- Jeremy Bentham
- Plato
- Socrates
- The Fox and the Lion - Niccolò Machiavelli - 마키아벨리의 재해석 [연세대 김상근 교수]
- Thomas Hobbes - Leviathan (a state of nature, absolute power, Leviathan)
- Voltaire and Leibniz - The best of all possible worlds?
- A Young Person's Guide to Philosophy
- Anaxagoras
- Aristotle
- Democritus
- Edmund Hussel
- Empedocles
- Epicurus and Lucretius (사물의 본성에 관하여)
- Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel
- Heracletos
- Hypatia
- Introduction to Diogenes the Cynic
- Introduction to Stoicism
- John Dewey
- Ludwig Wittgenstein
- Parmenides
- Plato
- Pre-Socratic Philosopher
- Schools of Philosophy - grouped by similar ideas
- Socrates
- Thomas Aquinas
- 에피쿠로스(Epicurus)의 행복론
- 에피쿠르스가 올았다
- academy of ideas.com
- Alfred North Whitehead
- Arthur Schopenhauer
- Baruch Spinoza - Ethics
- Big Ideas for Little Kids 1
- Confucianism
- Crash Course Philosophy
- Frankfurt School (프랑크푸르트 학파)
- Friedrich Nietzsche
- General (철학 일반)
- Good News For Anxious Christians - Phillip Cary
- History of Philosophy - King's College London
- Immanuel Kant
- Jean-Paul Sartre for Biginner
- John Locke
- Kierkegaard "이것이냐 저것이냐" 읽기
- Kierkegaard for Beginner
- Consciousness is the Problem (Descartes)
- Death and Existence as Subjective Truth
- Despair (Sickness onto Death)
- Dread or Anxiety (The Concept of Dread)
- from Either/Or - the story of Don Giovanni (Silhouettes)
- Indirect Communication
- Objective and Subjective Truth (Postscript)
- The Reason why Jesus speaks only in parables
- The Three Forms of Existence (Either/Or)
- 키르케고르 <죽음에 이르는 병>
- 파우스트 줄거리
- Michael Sandel - What is Justice Series (Harvard University)
- Episode 01 - Justice: What's The Right Thing To Do? (Trolley story)
- Episode 02 - Putting a price tag on life
- Episode 03 - Free to choose
- Episode 04 - This land is my land
- Episode 05 - Hired gun
- Episode 06 - Mind your motive
- Episode 07 - A lesson in lying
- Episode 08 - What is fair start
- Episode 09 - Arguing affirmative action
- Episode 10 - The good citizen
- Episode 11 - The claims of community
- Episode 12 - Debating same sex marriage
- Michael Sandel: The lost art of democratic debate
- Michel Foucault
- Nicomachean Ethics - Aristotle
- Philosophers
- Alfred North Whitehead
- Aristotle (384 ~ 322 B.C.)
- Aristotle Video Lecture
- Aristotle's Lagoon (2010)
- Arthur Schopenhauer (Youtube 책사람)
- Cicero
- David Hume
- Francis Bacon - 경험론(Empiricism)의 창시자, 베이컨의 4가지 우상
- Fredric Nietzschear - The Death of the Father
- Kierkegaard - Sea of Faith - BBC documentary
- Kierkegaard - 죽음에 이르는 병 The Sickness Unto Death
- Philosophers and Kings: Plato's Republic
- Plato (424 ~ 347 B.C.)
- Plato's The Myth of the Cave - from The Republic
- Plato's The Republic Summary
- Plotinus (204/5 – 270 C.E.)
- Schelling (1775 – 1854)
- Schopenhauer - Idea of the Will
- Socrates (468 ~ 399 B.C.)
- Søren Kierkegaard (1813 – 1855)
- 파스칼이 만난 하나님
- Philosophers for Kids
- Philosophical Foundations for Christian Worldview
- Political Science or Philosophy
- Rene Descartes - Meditation on First Philosophy
- Rousseau
- The Examined Life - Advanced Philosophy for Kids
- The Great Guide (What David Hume can teach us abut being human and living well)
- The Moral Responsibility of Modern Man Erich Fromm
- The Philosopher's Toolkit
- The Story of Philosophy - Bryan Magee
- Aristotle (384 BC – 322 BC)
- Copernicus to Galileo
- Descartes
- Diogenes - The Cynics
- Francis Bacon
- Isaac Newton
- Johannes Kepler (케플러 1,2,3법칙)
- John Locke - Empiricists (The Supreme Liberal)
- John Locke – A Philosophical Founder of America
- John Locke and The Enlightenment by Oxford Observer
- Leibniz
- Machiavelli
- Medieval Philosophy
- Plato (428 BC – 348 BC)
- Saint Augustine
- Saint Augustine - Neoplatonism and Christianity
- Saint Augustine’s Neo-Platonism
- Socrates (470 B.C. ~ 399 B.C.)
- Spinoza
- The Epicureans
- The Sceptics
- The Stoics (Stoicism)
- Thomas Hobbes (만화)
- Western Philosophy - An Anthology, John Cottingham
- You Shall Be As God - Erich Fromm (interpretation of O.T.)
- A Little History of Philosophy - Nigel Warburton
- Psychology
- Albert Bandura - Moral Disengagement: How People Do Harm and Live with Themselves
- Anna Freud - The Ego and the Mechanisms of Defense
- Arrested Development (발육지체, 정지, 저해)
- Carl Gustav Jung (1875 ~ 1960)
- D.W. Winnicott - Home is Where We Start From
- Emotional Intelligence - Daniel Goleman (1995)
- Erich Fromm - Escape from Freedom (자유로부터 도피)
- Erich Fromm - The Art of Loving
- Introduction (사랑은 기술인가?) (1956)
- Love's Disintegration in Western Society
- Love's Disintegration in Western Society 2
- The Theory of Love 1 - Symbiotic union(공생관계), Spinoza (passive or active affects), Giving
- The Theory of Love 2 - 4 Elements of Love,
- The Theory of Love 3
- The Theory of Love 4 - Love of God (Motherly love and Fatherly love)
- The Theory of Love 5
- 그리움의 사랑과 성실한 사랑 (Love with longing and love with faithfulness)
- 무모한 결정은 나쁜 결정이 아니다.
- 사랑에 대해서 배워야할것이 없다고 생각하는 이유?
- 사랑의 기술 - 하트가 불러온 오해
- Erich Fromm - To Have or To be
- [현대의 고전] 1 에리히 프롬, 『사랑의 기술』
- 3. Having and Being in the Bible
- 4. What is the Having Mode?
- 5. What is the Being Mode
- 6. Further Aspects of Having and Being
- Erich Fromm
- Erich Fromm - 1부 인간본성은 있을까? 있다면 무엇일까?
- Having and Being in Daily Experience
- Introduction
- The Importance of the Difference between Having and Being
- 결혼은 왜 미친 짓일까?
- 사랑의 기술 - 하트가 불러온 오해
- 소유냐 존재냐 - 1. 문제의 제기
- 소유냐 존재냐 - 2. 인문학적 윤리란? (Humanistic Ethics)
- Erich Fromm - 우리는 여전히 삶을 사랑하는 가
- Feeling Good Together - David D. Burns
- General or Introduction
- Grit
- Habitus (아비투스)
- Jacques Lacan (자크 라캉)
- John Bowlby - Separation (Anxiety and Anger)
- Jordan Peterson
- Lack of Commitment
- Living from the Center: Spirituality in an Age of Consumerism
- Melanie Klein - The Psychoanalysis of Children
- Personality and Disposition (성격과 기질 이론)
- Quite - Susan Cain
- Reinventing Your Life - Jeffrey E. Young
- Schema Theraphy - Jeffrey E. Young
- The Death of Sigmund Freud - Mark Edmundson
- The Evolution of Desire - David M. Buss
- The Triarchic Mind - Robert J. Sternberg
- Thinking, Fast and Slow - Daniel Kahneman
- What is Psychotheraphy? - The School of Life
- Will to Believe - James William
- 김경일 - Sapience Studio
- 김창옥 TV
- 나는 왜 네 말이 힘들까 - 박재연
- 엄마의 말하기 연습 - 박재연
- Albert Bandura - Moral Disengagement: How People Do Harm and Live with Themselves
- Research
- Black Swan - Nassim Nicholas Taleb
- How to Improve Your Critical Thinking & Reflective Skills
- How to Write Better Essay - Bryan Greetham
- 1. Interpretation of the Question (Concepts)
- 12. Reading Purposefully
- 15. Remembering Your Notes
- 16. Note-taking for criticism and evaluation
- 2. Practical Examples (concepts) - Authority and Power
- 3. Learning to Analyse
- 4. The Three Steps Technique
- 5. Creating Your Own Concept
- Chapter 13. Processing the ideas
- Chapter 16. Note-taking for criticism and evaluation
- Note-taking Skill - Bryan Greetham
- Stage 4 Writing
- Types of Essay
- What is plagiarism?
- Why write essay?
- Quality Research Papers
- Reflective Writing Exampes
- Research Topics
- Smart Thinking - Bryan Greetham (how to think conceptually)
- Speed Reading - Nathan Armstrong
- The Craft of Research
- The Study Skills Handbook - Stella Cottrell
- University of Hull
- www.irisreading.com (Speed Reading & Comprehension)
- Science
- Self-Improvement (자기 계발)
- Sermon Library
- Bill Hybels
- Leadership Summit 2003 - Passing the leadership test
- Leadership Summit 2003 - The leaders edge
- Leadership Summit 2006 - Life cycle of leader
- Leadership Summit 2006 - The Power of Clarity
- Leadership Summit 2007 - Vision To Die For
- Leadership Summit 2007 - Whatever You Do Inspire Me
- Leadership Summit 2010 - Holy Discontent
- Leadership Summit 2010 - The Power of Whisper
- Leadership Summit 2011 – 5 Critical Questions
- Billy Graham
- 2. The Indestructible Bible - Billy Gram: The Inspirational Writings
- Choices (1981)
- How to live Christian Life (1957) - New York Crusade
- The Great Quest - Billy Gram: The Inspirational Writings
- The Holy Sprit and You (1983)
- The Offence of the Cross (1958)
- Three Things You Cannot Do Without
- Who is Jesus?
- Charles Spurgeon
- Daniel Kim
- For my kids
- John Maxwell
- John Wesley
- Martin Luther
- Rick Warren
- Being Thankful Even In Bad Times
- If I Could Only Teach You One Thing: Why God Made You with Rick Warren
- Pastor Rick Warren Compares Life to a Game of Poker - Oprah's Lifeclass
- Pastor Rick Warren on the 5 Things That Shape You - Oprah's Lifeclass
- Rick Warren: How to Stay Relevant
- Winning With The Hand You're Dealt with Rick Warren
- Rick Warren - Preaching for Life Change
- 강준민목사 아가서 강해
- 온누리교회 집회및 하용조목사
- 30대 남성을 위한 집회
- 30대 남성을 위한 집회 - 챔피언 1막 (The Power)
- 30대 남성을 위한 집회 - 챔피언 1막 특별간증
- 30대 남성을 위한 집회 - 챔피언 2막 (The Pro)
- 30대 남성을 위한 집회 - 챔피언 3막 (The Passion)
- 30대 여성을 위한 전도 집회
- 30대 여성을 위한 전도 집회 - 프로포즈 1막 사랑이야기
- 30대 여성을 위한 전도 집회 - 프로포즈 2막 결혼이야기
- 30대 여성을 위한 전도 집회 - 프로포즈 3막 행복이야기
- 맞춤전도 - 가정사역을 통한 전도 (권준목사)
- 맞춤전도 - 내적치유를 통한전도 (유진소목사)
- 하용조 목사님 설교
- 하용조 목사님 설교 - 교회 부흥의 비결
- 하용조 목사님 설교 - 성령을 사모하라
- 하용조 목사님 설교 - 성령집회 부흥의 불
- 하용조 목사님 설교 - 예수님이 꿈꾸시는 교회
- 이용규선교사님 집회 동영상
- 전병욱목사 (홍대새교회)
- 전병욱목사 설교모음
- 강점을 가지고 일하라 1
- 강점을 가지고 일하라 2
- 강점을 가지고 일하라 3
- 강점을 가지고 일하라 4
- 거친 야성의 남자들이 몰려드는 교회 2006
- 기질설교 - 남자를 미치게 하는 우울질 여자
- 기질설교 - 남자위에 군림하는 담즙질 여성
- 기질설교 - 다혈질 여성과 행복하게 사는 남자들의 길
- 기질설교 - 답즙질남성 리더십과 일중독
- 기질설교 - 우울질 남성의 용의 주도함과 어두움
- 기질설교 - 우울질 여성의 매력과 한계
- 로마서강해 - 남을 판단하는 사람의 심리상태
- 로마서강해 - 딜레마를 품어주는 남은 자
- 로마서강해 - 딱딱하지만 신학을 알아야할 이유
- 로마서강해 - 반복된 사랑은 변화를 일으킨다
- 로마서강해 - 사랑의 힘을 과소평가하지 말라
- 로마서강해 - 은혜는 시각과 힘을 변화시킨다
- 로마서강해 - 이중성을 숨기는 교묘한 시도들
- 로마서강해 6 - 신앙은 종교기계가 되는 것이 아니다
- 사도행전 29 - 성격적 열심은 진짜 믿음이 아니다
- 사도행전 36 - 믿는것 이상으로 살 수 없다
- 사도행전 5 - 니들이 교회가 뭔지 아냐?
- 사도행전 59 - 딱딱하면 죽고 유연하면 산다
- 사도행전 63 - 빠른 변화 강력한 변화를 일으키는 법
- 사도행전 70 - 통찰력을 기르면 일이 이루어진다
- 사도행전13 - 기독교는 항상 핍박 당하는가?
- 사도행전15 - 이성과 자율성을 잃으면 신앙은 끝이다
- 사도행전34 - 진실보다 강한 힘은 없다
- 시편강해 10 - 악인의 팔을 꺽으소서
- 시편강해 11
- 시편강해 12
- 시편강해 13
- 시편강해 14
- 시편강해 15
- 시편강해 17
- 시편강해 18
- 시편강해 19
- 시편강해 20
- 시편강해 22 - 거절감의 고통 (The pain of rejection)
- 시편강해 23
- 시편강해 25
- 시편강해 26
- 에베소서강해 1
- 에베소서강해 2
- 에베소서강해 3
- 에베소서강해 4
- 에베소서강해 5
- 에베소서강해 6
- 청년부흥집회 - 균형있는 신앙의 3가지 요소(1)
- 청년부흥집회 - 균형있는 신앙의 3가지 요소(2)
- 청년부흥집회 - 은혜를 아는 자가 되라 (1)
- 청년부흥집회 - 은혜를 아는 자가 되라 (2)
- 청년부흥집회 - 존귀한자가 되라(1)
- 청년부흥집회 - 존귀한자가 되라(2)
- 핵심전달에 실패하면 거품사역이 된다 2005
- 전병욱목사 설교에서 인용한 책들
- 주제별 설교 모음
- 한경직 목사
- Bill Hybels
- Sociology and Political Writings
- Spiritual Readings
- A.W. Tozer
- Church History
- Dallas Willard
- Dietrich Bonhoeffer
- J Grasham Machen
- Jonathan Edwards
- Philip Yancey
- Phillip Cary
- Purpose Driven Church
- Purpose Driven Life
- Purpose Driven Life 1 - You were planed for God's pleasure (Worship)
- Purpose Driven Life 2 - You were formed for God's family (Fellowship)
- Purpose Driven Life 3 - You were created to become like Christ (Discipleship)
- Purpose Driven Life 4 - You were shaped for serving God (Ministry)
- Purpose Driven Life 5 - You were made for mission (Mission)
- St. Augustine
- Augustine and Platonism
- Augustine and the Platonists
- Love One Another, My Friend - Chapter 12 "Unanswered Prayer"
- Love One Another, My Friend - Chapter 14 "God is Love"
- Love One Another, My Friend - Chapter 20 "Love Casts Out Fear"
- On Free Choice of the Will (Augustine) - Peter King
- Saint Augustine - Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
- St. Augustine’s Concept of Disordered Loves and its Contemporary Application
- The City of God (하나님의 도성, De civitate Dei, 신국론)
- The Confession 7 - The Problem of Evil and Free Will
- The Confessions
- The Problems of Augustine's Theology (어거스틴 신학의 문제점)
- 성 어거스틴의 생애와 사상
- The Road to Character - David Brooks
- The Spirit of the Child
- Worship Series
- 영성과 기도훈련
- 예배와 제자훈련
- Summer Camp Curriculum
- 6 Most Important Decisions You Will Ever Make
- 7 Habits of Highly Effective Teens
- Biography
- College Advisor
- 2021 Best Colleges for Art in America
- Glasgow University in Scotland
- Phillips Academy
- Phillips Exeter Academy
- The 50 Best Boarding Schools in the U.S.
- The Effects of Music on a Student's Schoolwork
- Top 10 Universities in UK
- Top Liberal Arts Colleges Rankings
- Top Universities
- University of Dundee -Scotish University
- Comic book, Drawing, Animation Presentation etc.
- EBS [사회탐구]윤리와 사상 - 강승희
- Education, The Importance of Learning, Motivation
- Eureka Math
- Finance and Accounting Fundamentals for Kids
- How to Argue
- How to Read a Book - Mortimer Adler
- How to Speak How to Listen - Mortimer Adler
- How to teach your children Shakespeare
- Humanities (지적 대화를 위한 넓고 얕은 지식) - History, Economy, Politics, Society, Ethics
- iMovie Essential Training
- Math for kids
- mrdowling.com
- Ancient Greece - Alexander the Great and Hellenism
- Ancient Greece - Aristotle
- Ancient Greece - Athens and Democracy
- Ancient Greece - Greek Mythology
- Ancient Greece - Persia and the Battle of Marathon
- Ancient Greece - Plato
- Ancient Greece - Socrates and Greek Philosophy
- Ancient Greece - Sparta
- Ancient Greece - The Cradle of Western Civilization
- Ancient Greece - The early Greece
- Ancient Greece - The Iliad and the Odyssey
- Ancient Greece - The Peloponnesian War and Thucydides
- Ancient Greece - The Poli
- Ancient Rome - A New Power Rises
- Ancient Rome - Caesar, Cleopatra and Marc Antony
- Ancient Rome - Julius Caesar
- Ancient Rome - Patricians and Plebeians
- Ancient Rome - The Punic Wars
- Oxford dictionary of proverbs
- Philosophy for Kids
- Part 1 - Values (Ethics)
- Question #1 - Plato Are you a fair and just person
- Question #10 - Do we controls technology or does technology controls us (Martin Heidegger)
- Question #11 - How do you know for certain that things move? (Zeno)
- Question #12 - What makes something you say true? (Aristotle)
- Question #13 - Can you doubt that you exist? (Rene Descartes)
- Question #14 - Does a tree make a sound if it falls in a forest with no one around (George Berkeley)
- Question #15 - Are you certain that the law of gravity is really a law (David Hume)
- Question #16 - How can you tell when you know something (Immanuel Kant)
- Question #17 - Can another person understand your feelings? (Ludwig Wittgenstein)
- Question #18 - Can you lie to yourself? (Jean-Paul Sartre)
- Question #19 - Do you perceive things as they are or only as they seem to be? (Bertrand Russell)
- Question #2 - Aristotle : How do you know who your friends are?
- Question #20 - Can computers think? (Daniel Dennett)
- Question #21 - Can you think about nothing at all? (Parmenides)
- Question #22 - Does anything ever happen by chance? (Democritus)
- Question #23 - What happens to numbers when you are not using them (Plato)
- Question #24 - Are numbers and people equally real? (Aristotle)
- Question #25 - Is time what you see when you look at a clock? (St. Augustine)
- Question #26 - if the universe came from the Big Bang, where did the big Bang come from? (Aquinas)
- Question #3 - Should you be rewarded for your efforts in school? (Confucius - result or effort)
- Question #4 - Should you let little things bother you? (Marcus Aurelis, Dudy)
- Question #5 - Is it your duty to give to charity? (Moses Maimonides)
- Question #6 - Will having fun make you happier than studying (John Stuart Mill - Happiness)
- Question #7 - Should you ever tell a lie (Immanuel Kant - end or means?)
- Question #8 - Are there times when you should be violent? (Martin Luther King, jr.)
- Question #9 - Do you sometimes feel weird when you are with others (Simone de Beauvoir)
- Political Science
- Powerpoint and Presentation Fundamentals
- Programming for Kids
- BlueJ and other Java education resources
- Foundations of Programming - David Gassner
- Greenfoot Tutorial 1 - Trick the Turtle (from #1 to #16)
- Greenfoot Tutorial 2 - Bouncy Coloured Balss (from #16 to 23)
- Greenfoot Tutorial 3 - Breakout Game (from #24 to 33) 벽돌깨기
- QuickTime Recording
- Raspberry pi
- Syllabus
- Reading
- 10 Tips to Improve Your Reading Comprehension
- Books, are the best of things.... (Ralph Waldo Emerson)
- Getting Back to Reading
- How To Improve Your Reading Comprehension
- Jordan Peterson On Importance Of Reading
- Obama Labor Day Address
- Proust and The Squid - The Story and Science of the Reading Brain
- Why Read? - Mark Edmundson
- Smrt English (English Writing and Essay)
- SSAT or ISEE
- Studio Recording with GarageBand
- The Story of Philosophy
- VideoScribe and Animated Presentation
- Create Your Own Custom Drawings for Whiteboard Video (iDraw)
- How to Design Your Own Whiteboard Animation
- How to Nail Your Next Presentation
- PowToon Examples
- RSAnimation (youtube channel) - Ken Robinson
- The Secrets Behind the Rise of Video Scribing
- The Seven Pillars of Storytelling
- VideoScribe Examples
- VideoScribe Tutorials
- Writing
- 10 Tips to Help Build Your Child’s Writing Skills
- Essay Sample Questions for SSAT or ISEE
- Good Essay Examples
- Helping Young Children Develop Strong Writing Skills
- Homeschool vs Public School
- How to print a booklet | lynda.com
- How to Write a Children's Book
- How to write a novel - Snowflake Method (Randy Ingermanson)
- How to Write Reflection Paper - University of Hull
- Learn How to Write Fiction - www.thebalancecareers.com
- Margaret Atwood - Creative Writing
- Natalie Goldberg - Writing Down The Bones
- Personal Narratives - Lessons and Examples
- Sample paper: Home School Secrets
- Sample Travel Blog 1
- Sample Travel Blog 2
- SSAT Answer Sheet
- SSAT Sample Test - from Ivy Global (ssatprep.com)
- Stephen King - On Writing: A Memoir of the Craft
- Summer Writing Ideas for Kids
- The Power of Writing - Jordan Peterson - Cannadian pyschologist
- Tips for Parents of Struggling Adolescent Writers
- Writing a Research Paper - Judy Steiner-Williams
- Writings from Skillsyouneed.com
- 마인드맵으로 일기 잘 쓰는 법, How to Write a Diary Entry (for children)
- The School of Life
- Dating
- Great Thinkers
- Anna Freud (Defense Mechanism)
- Capitalism
- Coco Chanel
- Donald Winnicott
- Friedrich Nietzsche
- Goethe 1
- Goethe 2
- Jane Austen - from School of Life
- Karl Marx
- Leo Tolstoy (1828 - 1910)
- Leo Tolstoy (톨스토이의 삶과 그의 작품세계)
- Marcel Proust (1871 - 1922)
- Niccolò Machiavelli
- On Being Nice - Good Listener
- Political Theory - Friedrich Hayek (신자유주의)
- Political Theory - John Maynard Keynes
- Sigmund Freud
- Virginia Woolf (1882 - 1941)
- How to find love
- On Being Nice
- On Confidence
- Relationship (Romanticism)
- Self-knowledge (자신의 심리적 상처, 자기인식)
- Simpler Life
- Stay or Leave (이혼을 할것인가 말것인가)
- 1. Is it okay to want them to change?
- 10. Who is rejecting whom?
- 11. Why do I continue to feel so stuck?
- 12. Why are they so puzzling?
- 13. What can you tell me to make me less scared of leaving?
- 14. Does it have to be tragedy?
- 15. But I don’t find them awful
- 16. Do I have a permission to do this?
- 17. Are my expectations too high?
- 18. How can I tell them?
- 19. How come they seem so lovely right now?
- 2. Are we just too different?
- 20. Why do I feel so nostalgic?
- 21. Is it OK to compromise?
- 22. How do I find a closure?
- 23. Are there alternatives to staying or leaving?
- 24. Am I making a terrible mistake?
- 3. Can people change? (사람이 변할 수 있나?)
- 4. Is it worth breaking up over sex?
- 5. What about the children?
- 6. Have we tried everything? (Couple Theraphy)
- 7. What if I end up lonely?
- 8. What if I just repeat the same mistakes?
- 9. Can I cope practically? (집안일과 돈버는 일)
- The Sorrows of Love
- Why we hate cheap things (Good Materialism)
- Why you will marry the wrong person
- Theology
- Adam, Eve, and the Serpent (원죄 교리의 기원)
- Anthropology
- Augustine's Invention of the Inner Self - Phillip Cary
- Bible Stories For Children
- Old Testament: The Nile Turns to Blood
- New Testament: A Child Is Born
- New Testament: Escape to Egypt
- New Testament: Jesus Calls His Apostles
- New Testament: Jesus Feeds the Multitudes
- New Testament: Miracles of Jesus
- New Testament: Temptations in the Desert
- New Testament: The Announcement to Mary
- New Testament: The Baptism of Jesus
- New Testament: The Crucifixion
- New Testament: The First Miracle
- New Testament: The Last Supper
- New Testament: The Resurrection of Jesus
- New Testament: The Trial of Jesus
- New Testament: Triumphant Entry into Jerusalem
- Old Testament: Abraham's Caravan
- Old Testament: Across the Red Sea
- Old Testament: Daniel and the King's Dreams
- Old Testament: David the Victorious
- Old Testament: Esau and Jacob
- Old Testament: Fire in the Desert
- Old Testament: Horeb, Mount of the Covenant
- Old Testament: Isaac and Ishmael
- Old Testament: Jerusalem Burns
- Old Testament: Joseph and the Pharaoh
- Old Testament: Moses, the Last Victory and Jericho
- Old Testament: Night of the Lamb
- Old Testament: Noah
- Old Testament: Prince Moses
- Old Testament: Samson and the Philistines
- Old Testament: Samuel - A King for Israel
- Old Testament: Saul is Defeated
- Old Testament: Sodom and Gomorrah
- Old Testament: Solomon and the Temple
- Old Testament: The Demise of Solomon
- Old Testament: The Prophet
- Old Testament: The Shattered Calf
- Old Testament: The Son of Terah
- Old Testament: The Sons of Jacob
- Old Testament: The Sons of Noah
- Old Testament: The Tower of Babel
- Old Testament: Twelve Tribes, One People
- Bible Story Videos for Kids
- Big Truths for Young Hearts
- Christian Theology - Alister Mcgrath
- Church Traditions and Denominations
- Ethics
- Gnostic Gospels (영지주의 복음서)
- Historical Event in Theology
- Jürgen Moltmann
- Psychology
- Question and Answer
- Melchizedek (멜기세덱)
- Not by Faith Alone: The Martin Luther Paradox
- Sola Fide: Salvation by Faith Alone
- The Difference Between Catholicism and Christianity
- The Holocaust from a scriptural perspective
- The Last Adam
- Why Cross? 왜 십자가라는 처형방법
- Why do Catholics worship Mary?
- Why is justification by faith such an important doctrine?
- Why the Firstborn Son? - 왜 장자를 바치라고 하셨을까?
- Rudolf Bultmann
- Sacraments and Spiritual Practice
- Sociology
- Thelogy by Theme
- Augustine on Genesis - The Literal Interpretation of Genesis
- Challenges of Process Theology
- Compare the Lutheran and the Roman Catholic
- Contemporary doctrine of the Trinity
- Debate Topic: Is the Trinity Doctrine Biblical?
- Doctrine of creation
- Early Trinitarian disputes
- Free Will Defense
- Image of God
- Infant Baptism, 유아세례? 침례 or 세례?
- Original Sin and Inherited Guilt
- Pelagius and Augustine debate over free will
- Sallie McFague¡¯s view on God and creation
- the monist, dichotomist or trichotomist
- The Problem of Evil: Irenaeus, Augustine, John Hick, Alvin Plantinga
- The theocentric pluralism of John Hick
- The True Origin of Easter by David C.Pack
- Thelology of Suffering
- Tradition and interpretation of Scripture
- What is systematic theology?
- What is the Classical Theism
- 니케아 회의와 삼위일체 논쟁
- 삼위일체 논쟁
- 성경신학과 조직신학의 차이점 (The Difference between Biblical Theology and Systematic Theology)
- 창세기의 창조에 대한 오해
- Theologians and Philosophers
- Abraham Kuyper (1837, 아브라함 카이퍼의 생애와 사역)
- Adolf Harnack - What is Christianity?
- Aristotle(아리스토 텔레스) (384 BC - 322 BC)
- Athanasius (AD 300)
- Augustin of Hippo (어커스틴) 354 ? 430
- cloudbiography.com
- Emil Brunner (에밀 브르너) 1889 - 1966 Swiss
- Foucault (푸코 1926 – 1984) - power is everywhere
- Friedrich Hegel (헤겔) 1770 - 1831
- Friedrich Schlerermacher (슐라이엘마허) (1768 – 1834)
- John Calvin
- John Calvin - Christian biographies for kids
- Jonathan Edwards (1703 - 1758)
- Karl Barth (칼 바트) 1886 - 1968 Swiss
- Lady Jane Grey
- Ludwig Feuerbach (포이어바흐) 1804 - 1872
- Martin Luther (1483 - 1546)
- Theology
- Against Calvinism - The Gospel Coalition
- Apostle's creed
- Dates of the New Testament Composition
- Evil and Human Suffering (악과 인간의 고통)
- Five points of Calvinism (칼뱅주의 5대 강령) - John Calvin
- General Philosophy
- Historical Event
- History 1
- Nicene Creed (니케아 신조)
- Philosopher 1
- Thelogians 1
- Theological Terms
- 여러가지 교회와 종파. 루터교, 장로교, 감리교, 오순절
- Theology for the Community of God (하나님의 공동체를 위한 신학)
- Third Millennium
- 개신대학원대학교 - 논문집
- 신학일반
- Calvinism vs Arminianism
- 자유주의 신학의 태동과 특징 - 안명준
- 한국 장로교 신학의 기원과 형성 - 문병호 총신대 조직신학교수
- 경건주의 (Pietism) 제2의 종교개혁
- 근본주의와 신복음주의 - 신복음주의의 입장
- 김동호 목사 “예정론, ‘칼빈주의 대표사상’ 아니다”
- 마틴 루터의 성경관 - 김명용
- 복음주의와 신복음주의, 복음주의와 근본주의, 복음주의와 개혁주의의 차이점
- 성경과 우주관 - 구약 시대의 우주관과 신관
- 성경과 우주관 - 신약시대의 우주관과 신관
- 성경의 무오(無誤, inerrancy)란 무엇을 말하는가? - 창조신학연구
- 성서무오설에 대한 오해 - 제자들의 교회
- 세대주의(Dispensationalism)
- 신복음주의 (New Evangelicalism) - David Cloud
- 신복음주의 (New Evangelicalism) - Paul Smith
- 신약성경 설교로서의 케리그마와 - 문상기 (침례신학대학교)
- 신정통주의 (Neo-Orthodox) - 칼 바르트의 신학
- 신정통주의 (Neo-Orthodox) 2
- 유럽신학의 근황 - 박아론 박사 (총신대 교수)
- 자유주의 신학과 성경해석 - 정중호 (두란노 빛과소금)
- 장신대의 신학과 신학노선
- 진보적 신학이란 무엇인가?
- 칼빈의 성경관과 주권사상 - 존 머레이
- 칼빈주의 예정론 비판
- 케리그마적 신학이란 무엇인가?
- 한국 장로교회의 분열에 대한 회고와 일치를 향한 전망 - 임희국 장신대교수
- 현대신학의 흐름 - 제 1장 유럽 신학
- 현대신학의 흐름 - 제 2장 미국 신학
- 예수냐 바울이냐 - 문동환
- 이 시대의 바른 기독교 사상 - 김명용
- 현대의 도전과 오늘의 조직신학 - 김명용
- Third Millennium Ministries
- Tim Keller
- Center Church
- Counterfeit Gods
- Chapter Five - The Power and The Glory
- Chapter Four - The Seduction of Success (Based on the story of Naaman and Elisha)
- Chapter One - All You've Ever Wanted (Based on Abraham and Isaac Story)
- Chapter Seven - The End of Counterfeit God (Based on the story of Jacob)
- Chapter Six - the Hidden Idols in Our Lives (Based on the story of Jonah)
- Chapter Three - Money Changes Everything (based on the story of Zacchaeus 삭개오)
- Chapter Two - Love is Not All You Need (Based on the story of Jacob, Rachel and Leah
- Epilogue - Finding and Replacing Your Idols
- Introduction - The Idol Factory
- Isaac’s Substitute Explained: Fear and Trembling
- Sermon about The Counterfeit God
- Debates and Public Speeches
- Encounters with Jesus - Sermon on the Gospel of John (요한복음 강해)
- 1. Skeptical Student - about Nathanael (Criticism about Moral Relativity)
- 10. The Courage of Mary (마리아의 4가지 반응, 왜 마리아는 믿기 힘들었나?)
- 2. The Insider and the Outcast - about Nicodemus and Samaritan Woman
- 3. The Grieving Sisters (Lazarus, Martha, and Mary, Incarnation, the problem of evil)
- 4. The Wedding Party (self-substitution, 어린양의 희생은 상징, 잔치가운데 죽음을 생각하시는 예수님)
- 5. The First Christian (What is faith? Mary at the tomb of Jesus, Resurrection)
- 6. The Great Enemy (about Satan, the doctrine of evil, 예수님의 시험)
- 7. The Two Advocates (Holy Spirt as the second Advocate, First Jesus)
- 8. The Obedient Master (Spiritual separation from God, 겟세마네동산에서 기도하시는 예수님)
- 9. The Right Hand of the Father (예수님의 승천)
- David Foster Wallace - Commencement Address - May 21, 2005
- Good Analogies by Tim Keller
- Good Definitions by Tim Keller
- Good Questions from Encounters with Jesus
- Every God Endeavor
- Frequent Reference by Tim Keller
- Difference between Religion and the Gospel (종교와 복음의 차이)
- Everybody worships. - David Foster Wallace
- Evidences that the Bible is the record of eye-witness
- From C.S. Lewis - How we related to God is like we relate to Shakespeare
- Good Questions from "King's Cross"
- Precious Remedies against Satan's Devices - Thomas Brooks
- Suggested Reading List
- The Resurrection of the Son of God - N.T. Wright
- Gospel in Life
- Session 1 - City (The World That Is)
- Session 2 - Gospel Repentance
- Session 2 - Heart (Three ways to live)
- Session 2 - The Gospel and the Heart
- Session 3 - Idolatry
- Session 4 - Community (The Context for Change)
- Session 5 - Witness (an alternate city)
- Session 6 - Tim Keller Sermon - Work (Cultivating the garden)
- Session 6 - Worldview
- Session 7 - The gospel and our neighbor
- Hidden Christmas - The Surprising truth behind the birth of Christ
- King's Cross
- 1. The Dance (Trinity) 마가복음 1장
- 2. The Calling (calling Disciples) - 복음의 의미, 종교와의 차이
- 3. The Healing (중풍병자를 고치신 예수님, your sins are forgiven. Why did he say that?)
- 4. The Rest (Sabath, 안식일의 의미, 종교와 복음의 차이)
- 5. The Power (폭풍을 잠재우신 예수님, 폭풍속의 요나와 예수님의 연결)
- 6. The Waiting
- Before (the Gospel of Mark is the testimony of Peter)
- The Book that Understand Me
- Living by Faith in Troubled Times (Sermon on Habakkuk 하박국)
- Making Sense of God
- Prayer - Experiencing Awe and Intimacy with God
- Preaching - Communicating Faith in an Age of Skepticism
- Preaching the Gospel in a Post-Modern World
- Redeemer City To City
- Sermon about the Problem of Pain
- Sermons
- Abraham's Prayer for the City
- Bible, means or end? (The OT is all about Jesus)
- David Prepares His People - The Ark of Convenant
- Evangelism - A Woman, a Slave, and a Gentile
- Generosity and Power - Zacchaeus (Luke 19:1 ~ 9)
- Hope for Your Life - The Gospel, Hope and The World - 1 Peter 1:3–13
- Leadership Summit - Prodigal God
- Parents and Children
- Perfect Freedom (How does the gospel changed me) - Romans 6
- Scripture - What is the bible?
- The Song of Creation - Sermon about Genesis 1
- Trinity - Father Son and Holy Spirit
- Sermons - Discovery: Can I believe
- Absolutism - Don't we all have to find truth for ourselves (Galatians 2:4-16)
- Authors@Google: Tim Keller
- Doubt What should I do with my doubts
- Evolution and Science
- Exclusivity - How can there be just one true religion (1 John 4 : 1~10)
- Hell - Isn't the God of Christianity an angry Judge (Luke 16: 19~31)
- How to Interpret the Bible (Are you a biblical literalist?)
- Injustice - Hasn't Christianity been an instrument for oppression (James 2:1~17)
- Literalism - Isn't the Bible historically unreliable and regressive (Luke 1:1-4; 24:13-32)
- Suffering - If God is good why is there so much evil in the world - (1 Peter 1:3~12)
- The Source of Faith - Converted by the Spirit (Acts 10:27~47)
- Sermons - Discovery: What is the gospel
- Sin as Broken Relationship - Sickness Unto Death
- Sin as Broken Relationship - The Healing of Anger
- Sin as Idolatry - The Struggle for love
- The Gospel Coalition - Part 1 : Confessional Statement
- The Gospel Coalition - Part 2 : Theological Vision for Ministry
- The Gospel Coalition - Part 3 : How should we relate to the culture around us
- The Gospel Coalition - Part 4 : What is gospel–centered ministry?
- The Prodigal God - And Kissed Him (Luke 15:11-24)
- The Prodigal God - Give Me Mine (Luke 15:11-14)
- The Prodigal God - He Came to Himself (Luke 15:11-20)
- The Prodigal God - He Welcomes Sinners (Luke 15:1-10)
- The Prodigal God - The True Older Brother (Luke 15:17-32)
- The Prodigal God - To Be Called Your Son (Luke 15:21-24)
- The Prodigal God - We Had to Celebrate (Luke 15:17-32)
- Understanding the Gospel - A Covenant Relationship (Deuteronomy 29:2-4, 9-21)
- Understanding the Gospel - How to Find the Way (Matthew 7:7-14)
- Understanding the Gospel - Predestination (1 Corinthians 1:18-31)
- Understanding the Gospel - The Gospel (Isaiah 53:4-11; 54:1-5,11-14)
- Understanding the Gospel - The Gospel Key to Change
- Understanding the Gospel - The History of Grace (Matthew 1:1-17)
- Understanding the Gospel - The Lost Ark (1 Samuel 5: 1-5; 2 Samuel 6: 1-15)
- Understanding the Gospel - The Prodigal Sons (Luke 15:1-2, 11-32)
- Understanding the Gospel - Union with Christ (Ephesian 2:4-10)
- Understanding the Gospel - What is gospel? - Leaders Guide
- Understanding the Gospel - What is The Gospel (Justified by Faith Romans3:21-28)
- Understanding the Gospel - What is The Gospel (Predestination 1 Corinthians 1:18-31)
- Sermons - Series by Theme
- About Jesus - Family of Jesus
- About Jesus - Jesus and the Bible
- About Jesus - Jesus as Father's Feast
- About Jesus - Jesus Meal with Matthew
- About Jesus - Jesus Meal with Peter
- About Jesus - On the mount Off the Mount
- About Jesus - The King on a Cross
- About Jesus - The Timing of Jesus
- Cultivating a Healthy Marriage part 1
- Cultivating Healthy Marriage Part 1
- Discipleship - Called To be Disciple (Mark 1 14 ~ 20)
- Esther and the Hiddenness of God - If I Perish I Perish (Esther 4:5~17)
- Job - A Path through Suffering (Miserable Comforter)
- Job - Questions of Suffering (Job 1:8~22)
- Parenting - Fathers Day Message
- Parenting - Parents and Child
- Practicing The Christian Life - Led by Spirit
- Practicing The Christian Life - Singing
- Practicing The Christian Life - Worship
- Spiritual Warfare 1 - The Death of Satan
- Spiritual Warfare 2 - How to be strong
- To an Unknown God (Acts 17: 13 ~ 34)
- The Reason for God
- 1. There Can't Be Just One True Religion
- 10. The Problem of Sin
- 11. Religion of the Gospel
- 12. The (True) Story of the Cross
- 13. The Reality of Resurrection
- 14. The Dance of God
- 2. How could a Good God Allow Suffering?
- 3. Christianity is a Straitjacket (구속하는 옷)
- 4. The Church is Responsible for So Much Injustice
- 5. How can a Loving God Send People to Hell?
- 6. Science Has Disproved Christianity
- 7. You Can't Take the Bible Literally
- 8. The Clue of God
- 9. The Knowledge of God
- Discussion 1: Isn't the Bible a Myth?
- Discussion 2: How can you say there is only one way to God?
- Sermon at Google by Tim Keller
- Western Classics
- Animal Farm - George Owell
- Anne Of Green Gables
- 11 Indispensable Life Lessons Every Woman Can Learn From ‘Anne Of Green Gables’
- Anne of Green Gables (1979) - Miyazaki Version
- Christ Blessing Little Children
- Heidi, Girl of the Alps (1974)
- Lucy Maud Montgomery
- Quotes About Anne Of Green Gables
- Reviews on Anne of Green Gable
- Why is Anne of Green Gables so popular
- Authors
- Brave New World - Aldous Huxley
- Cicero - Selected Works
- Classics to read aloud to your children
- Dialogues by Plato
- Fernand Braudel (French historian) 물질문명과 자본주의
- Francis Bacon - Novum Organum (신기관)
- Friedrich Nietzsche
- Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel
- Greek Mythology
- Antigone
- Aphrodite - goddes of love
- Apollo - god of music, truth and prophecy, medicine, the sun and light, poetry, reason and more
- Ares - god of war
- Artemis - goddess of the hunt carrying a bow and arrows
- Athena - goddess of wisdom and strategy
- Danaë, Perseus, Andromeda, Pegasus
- Dionysus - the god of wine, the youngest of the Olympians
- Dionysus or Bacchus
- Eco, Pan and Narcissus
- Europa. the continent Europe was named after her
- Hades - lord of the dead
- Hermes - god of transitions and boundaries
- Noah's flood and Deucalion's flood
- Orion
- Orpheus and Eurydice
- Persephone - the queen of the underworld. The Myth of Four Season
- Poseidon - lord of sea, moody and violent
- Prometheus - stole fire, and Pandora
- The Bible and Greek Mythology (Differences)
- The Bible and Greek Mythology (Similarities)
- The names of gods in Greek and Latin
- The Story of Oedipus: the King of Thebes
- The Story of Perseus
- Theseus and Minotaur
- Why is Greek mythology so important?
- 종교가 잉태한 철학; 오르페우스교로부터
- Herodotos' History
- Immanuel Kant
- Jean-Jacques Rousseau - The Social Contract
- Emile or Education (Summary and Analysis)
- Emile or Education (한국어 블로그)
- His Life from Stanford Philosophy
- Jean-Jacques Rousseau - His Life and Works
- Quotes from Jean-Jacques Rousseau
- Rousseau - Social Contract (만화)
- Rousseau’s Discarded Children
- Social contract theories by Hobbes, Locke, and Rousseau
- The Confession (고백록)
- The Origin of Inequalities
- The Social Contract
- Theatre, Calvinism, and Civil Society in Eighteenth-Century Edinburgh and Geneva
- 루소의 생애, 루소의 사상, 루소의 저작
- 루소의 에밀 요약정리
- John Locke - Second Treatise of Government
- John Milton - Paradise Lost
- John Stuart Mill - On Liberty
- Chapter 1. Introductory
- Chapter 2. Of the Liberty of Thought and Discussion.
- Chapter 3. Of Individuality, as one of the Elements of Well-being
- Chapter 4. Of the Limits to the Authority of Society over the Individual.
- Chapter 5. Applications
- How Does Conformity Influence Behavior?
- Introduction and the contents
- John Stuart Mill (1806 ~ 1873)
- Marcus Aurelius
- On Liberty (자유론 만화)
- Quotes - John Stuart Mill
- The Tyranny of Majority(다수의 횡포)
- The Tyranny of Majority(다수의 횡포)
- Utilitarianism
- Utilitarianism 2
- Wilhelm von Humboldt
- 대의정부론(Representative Government)
- Karl Marx
- Communist Manifesto(원숭이도 이해하는 공산당선언) 1 - Bourgeois and Proletarians
- Communist Manifesto(원숭이도 이해하는 공산당선언) 2 - Proletariats and Communists
- Karl Marx (만화 - 마르크스 자본론 2)
- Karl Marx (만화 - 마르크스 자본론)
- Karl Marx from "Big ideas simply explained"
- Karl Marx in 90 minutes
- Karl Marx, Jenny von Westphalen and Engels On Love and Marriage
- Karl Marx(만화 - 마르크스 자본론 3)
- On The Jewish Question (1843) 유대인 문제에 관하여
- Quotes from Karl Marx
- The Communist Manifesto (PDF)
- 인류에 가장 큰 영향을 끼친 책, 칼 마르크스의 『자본론』 | EBS Documentary
- 칼 막스 (대학생을 위한 서양철학사)
- Leviathan - Thomas Hobbes
- Literature Classics
- 19세기 영문학(English Literature in 19C)
- Alice in Wonderland Study Questions
- Alice's Adventures in Wonderland - Lewis Carroll
- Animal Farm - George Owell
- Anna Karelenina (톨스토이 성장을 말하다)
- Don Quixote
- Faust (괴테와 여인들)
- Great Expectation (위대한 유산)
- Jane Eyre - Charlotte Bronte
- Julie (신 엘로이스) - 첫눈에 반한다는 것
- Lady Chatterley's Lover (1928)
- Les Miserable (레 미제라블)
- Madame Bovary (마담 보바리)
- Moby-Dick by Herman Melville
- Oliver Twist - Charles Dickens
- Pride and Prejudice (오만과 편견)
- Sense and Sensibility
- The Count of Monte Cristo - Alfredo Dumas
- The Decameron by 조반니 보카치오
- The importance of classical literature
- The Secret Garden - Frances Hodgson Burnett
- The Secret Garden - Frances Hodgson Burnett
- The Sorrows of Young Werther (젊은 베르테르의 슬픔)
- The Wind in the Willows
- Why is Alice in Wonderland famous?
- 도스토옙스키 [죄와 벌]
- 왜 고전을 읽어야 하는가
- Nicomachean Ethics - Aristotle
- Nicomachean Ethics - Aristotle
- Politics - Aristotle
- Rene Descartes - Discourse on Method (방법서설)
- Rhetoric / Poetic - Aristotle (수사학 / 시학)
- Spinoza - Ethics, Theological-Political Treaties
- The History - Herodotus
- The Pilgrim's Progress
- The Prince - Machiavelli
- The Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism
- Karl Marx and Max Weber on social class.
- Max Weber: Summary from the School of Life
- Part 1: The Problem - Luther's Concept of Calling
- Part 1: The Problem - Religious Affliction and Social Stratification
- Part 1: The Problem - The Spirit of Capitalism
- 금욕적 프로테스탄티즘의 직업윤리 - 사회사/역사사회학, 타인의 연구
- 막스 베버와 프로테스탄트의 윤리와 자본주의 정신
- 수도원 안의 금욕주의가 세속으로
- 프로테스탄티즘의 윤리와 자본주의 정신 (The Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism)
- The Republic - Plato
- The Social Contract and the Discourses - Jean-Jacques Rousseau
- The Trojan War - The Iliad of Homer
- Thomas Hobbes - Leviathan
- Voltaire
- Works of Shakespeare
- YouTube Contents
- 도올 김용옥
- Analects (논어)
- Analects - Book 2 (위정편) 1
- Analects - Book 2 (위정편) 2
- Analects - Book 2 (위정편) 3
- Analects - Book 3 (팔일편) 1
- Analects - Book 3 (팔일편) 2
- Analects - Book 3 (팔일편) 3
- Analects - Book 4 (리인편) 1
- Analects - Book 4 (리인편) 2
- Analects - Book 4 (리인편) 3
- Analects - Book 5 (공야장) 1
- Analects - Book 5 (공야장) 2
- Analects - Book 5 (공야장) 3
- Analects - Book 6 (옹야편) 1
- Analects - Book 6 (옹야편) 2
- Analects - Book 7 (술이편) 1
- Analects - Book 7 (술이편) 2
- Analects - Book1 (학이편) 1
- Analects - Book1 (학이편) 2
- Favorites: 호학, 恕, 聞一知十
- 만화 논어 - Human Civilizations
- 강신주의 장자 수업
- 강연 (Lectures)
- [유시민의 알릴레오 31회] 유시민이 묻고 도올이 답하다 - 10.4 12주년 특별강좌 3강
- JTBC 차이나는 도올 (2016)
- 중국과 세계질서 재편1 - 25년만의 고대강의
- 천년의전라도 청춘,세계를 품다 1부
- 철학의 갈래 - 비판철학과 사변철학
- 철학의 주요한 문제들 - 지식과 존재, Good & Evil
- 기독교와 중국선교의 시작(Nestorianism)
- 기독교와 한국현대사 (이승만, 서재필, 대한민국, 대한제국, 배제학당, 한일합병)
- 김용옥 교육입국론 (2014) 순천대학교 우석홀 (전라남도 교육청)
- 뉴스공장 스튜디오를 쑥대밭으로 만든 도올 김용옥 선생님
- 도올 김용옥의 교육입국론 특강
- 도올 김용옥의 논어특강 1부
- 도올 김용옥의 논어특강 2부
- 도올, 직지를 말하다 (직지심경) - 고려의 문명과 역사, 불교
- 도올특강 - 종교란무엇인가? (원광대하교 강의)
- 도올학당 수다승철 2강 (사랑에 관하여)
- 도올학당 수다승철 9편
- 도올학당 수다승철 9편 - 장자 기심(機心)은 순백(純白
- 배움의 즐거움 - 도올의 인생이야기
- 수원의 꿈과 정조 1 사도세자의 죽음과 화성 건축
- 우리는 누구인가 제17강 - 기와 정치(최한기), 주어부 술어부
- 우리는 누구인가 제20강 - 수운(水雲) 최수훈
- 우리는 누구인가? - 정도전
- 율곡 이이 의 격몽요결 (擊蒙要訣)
- 중국과 세계질서 재편1 - 25년만의 고대강의
- 지금 왜 다산인가? 1 - 정약용의 문제의식과 기독교
- 청소년을 위한 [동양고전특별강연]
- 교육입국론
- 기독교성서의 이해
- 노자강연(국립극단) + 만화 노자
- 국립극단 노자강연 1 노자라는 시니피앙과 연극이라는 시니피에
- 국립극단 노자강연 2 세종 한글, 선조 임진왜란
- 국립극단 노자강연 3 헤겔 맑스 니체 프로이드 그리고 노자
- 국립극단 노자강연 4 노자는 인류사상의 원점
- 국립극단 노자강연 5 - 사림과 경화 사족
- 국립극단 노자강연 6 - 아름다움과 추함, 생이불유 공성이불거
- 국립극단 노자강연 7 - 우리의 역사를 제대로 알아야겠다
- 국립극단 노자강연 8 - (마지막회) 조선의 얼이여 영원하리!
- 노자사상과 서양철학 비교 (부분과 전체)
- 만화 노자
- 만화 노자 10 - 지나친 욕심은 위험하다 (제자백가)
- 만화 노자 11 - 부드러움이 강함을 이긴다. (柔之勝剛)
- 만화 노자 12 - 이세상에서 가장 귀한 보배
- 만화 노자 3 -
- 만화 노자 4 -
- 만화 노자 5 - 성인은 모든것을 상대적으로 본다
- 만화 노자 6 - 성인은 자랑하지 않는다
- 만화 노자 7 - 칭찬과 비난에서 자유로운 사람 (寵辱若驚)
- 만화 노자 8 - 훌륭한 지도자
- 만화 노자 9 - 진실로 현명한자 진실로 위대한자
- 만화 논어 2 -
- 소쉬르 시니피앙 시니피에 (데리다 해체이야기)
- 노자강의 - 최진석
- 노자와 21세기
- 논술과 철학강의 1 (2006)
- 논술과 철학강의 2 (2006)
- Definition of Philosophy. Conceptual Thinking (철학에대한 정의, 철학은 무전제의 사고)
- Epistemology: A Priori vs. A Posterior; Analytic vs. Synthetic; Necessary vs. Contingent
- Harry Elkins widener memorial library
- Platonism (관념론)
- 라오주앙철학(노장사상), 철학과 신학
- 베이컨의 우상론 (Bacon's Four Idols)
- 삼단논법의 결함, Anselm's Ontological, Teleological, Design Arguments
- 신발과 발, 기철학, 몸철학 (You need to be dumb to do philosophy)
- 정치와 종교, 사물적지식, 사리적지식, 수학의 중요성
- 철학은 절대를 추구하지 않는다 (Philosophy and Absolute Truth)
- 플라톤의 동굴의 우상 (Allegory of Cave)
- 논술세대를 위한 철학교실 (YouTube)
- 1. 3.1운동정신과 논술
- 10. 원자론의 탄생
- 11. 물리의 세계
- 12. 상대론과 발생학
- 13. 웃음이란 무엇인가?
- 14. 플라톤과 노자
- 15. 우리사회의 미래
- 16. 무명과 무욕
- 17. 건강과 의료제도
- 18. 진리와 아름다움
- 2. 생각이란 무엇인가? (논술의 의미)
- 21. 아일랜드 이야기
- 22. 필 인더 블랭크
- 24. 일상생활의 지혜
- 25. 연극이란 무엇인가?
- 26. 빔의 철학
- 27. 좋은글쓰기
- 29. 아리스토텔레스 철학
- 3. 존재란 무엇인가?
- 30. 태극기와 알렉산더
- 4. 헬라스적 사유의 역사적 배경
- 5. 새만금과 논술
- 6. 플라톤과 수학
- 8. 술과 수학 - 희랍철학, 존재론, 수학과 술의 관계
- 9. 아르케의 추구
- 논어관련 배경지식 (보현TV)
- Map of Spring Autumn Age (춘추 전국 시대)
- Max Weber’s View of Religion in China
- 공자사상과 계몽주의
- 공자의 제자들 - 자로, 안회, 자공, 자하, 자장, 유자
- 논어 해석의 역사. 주자학의 발전. 고주와 신주의 차이.
- 논어해석사
- 막스 베버의 군자불기 비판
- 사과십철, 공문십철
- 선양의 문제와 맹자의 역사의 도덕화 (from 만화맹자 2)
- 시경(詩經)
- 시경(詩經)에서 유래된 고사성언
- 신종추원 민덕귀후의 (愼終追遠 民德歸厚矣) - 제사
- 양주의 위아설, 묵적의 겸애설, 맹자
- 위대한 스승 공자
- 중국의 역사는 동아시아 역사다 - 대학 8강 / 2부 (고대중국역사)
- 춘추전국시대 막장 비극의 서막 (노나라 삼환의 역사)
- 하은주 삼애 (만화맹자 2)
- 달라이 라마와 도올의 만남
- 도마복음 강해
- 도마복음 강해(YouTube)
- 도올 시진핑을 말하다
- [역사란 무엇인가] "과거와 현재의 끊임없는 대화" E.H. Carr
- 먼나라 이웃나라 중국 제10강
- 먼나라 이웃나라 중국 제11강
- 먼나라 이웃나라 중국 제12강
- 먼나라 이웃나라 중국 제1강 - Synchronic and Diachronic
- 먼나라 이웃나라 중국 제2강 - 중국개혁을 향한 첫걸음 : 원로정치 폐지
- 먼나라 이웃나라 중국 제3강 - 시진핑의 아버지 시종쉰
- 먼나라 이웃나라 중국 제4강
- 먼나라 이웃나라 중국 제5강
- 먼나라 이웃나라 중국 제6강
- 먼나라 이웃나라 중국 제7강
- 먼나라 이웃나라 중국 제8강
- 먼나라 이웃나라 중국 제9강
- 시진핑 후기 5년 중국의 핵심 2
- 시진핑 후기 5년 중국의 핵심 2 - 기소불욕 물시어인
- 시진핑 후기 5년 중국의 핵심 2 - 왕꾸어웨이는 어떤 사람인가?
- 시징핑 후기 5년 중국의 핵심 1
- 인물들
- 중국현대사 - 대약진운동, 문화혁명의 홍위병
- 마가복음 강해
- 1장 예수는 갈릴리 사람
- 1장. 세례를 받으신 예수, 광야에서 받으신 유혹
- 2장 중풍병자를 고치신 예수, 안식일의 주인
- 3장 갈릴리사역의 확대
- 4장 하나님 나라에 관한 예수의 비유
- 5장 돼지떼 속으로 들어가는 마귀
- 5장 야이로의 딸, 혈루증 여인
- 6장 고향에서 존경받지 못하는 예수
- 6장 오병이어 Jesus feeds the five thousands
- 7장 손씻지않음
- The Birth Story of John The Baptist and Jesus(The Gospel of Luke)
- The Map of Ancient Israel
- 마가(John Mark)는 어떤 사람이었나?
- 메시아의 비밀, William Wrede's Messianic Secret
- 바울의 사도권
- 예수는 유대인인가 (Ancient Israel Map)
- 종교개혁 500주년 '미완의 종교 개혁' - 위르겐 몰트만, 도올 김용옥
- 총론
- 한국속담 (Korean Old Sayings)
- 맹자만화
- 맹자사람의 길
- 1. 양해왕, 양양왕
- 10. 만장상 - 대효종신부모, 노이불원, 가이해우, 서불진언, 처인천의, 진이예 퇴이의, 가도입명
- 11. 만장하 -
- 12. 고자 상 -
- 13. - 고자 하
- 14. 진심 상 -
- 16. 진심 하 -
- 2. 제선왕 양혜왕과 상왕 (도올의 맹자강의)
- 3. 양혜왕 하 - 여민동락, 사대주의, 낙이천하, 유련황망, 환과독고, 소위고국, 약시우강
- 4. 공손추 상 - 관중안자, 호연지기, 이력가인, 존현사능, 측은지심, 시인함인
- 5. 공손추 하 - 소불소지신, 여유작작, 맹자엄마, 불감청이 고소원, 천장부, 농단, 맹자거제
- 6. 등문공 상 - 맹자도성선, 약약불명현, 유항심, 학교, 인륜, 유신, 상부상조, 분분, 부자유친, 박장후장
- 7. 등문공 하 - 왕척이직심, 대장부, 통공역사, 식지야 식공야, 일치일란
- 8. 이루상 -
- 9. 이루하
- Font test
- 맹모삼천지교, 맹모단기, 맹모가돈육 - 맹자의 왕도사상
- 맹자는 누구인가? 맹자와 조기, (만화영화)
- 맹자의 몸철학
- 맹자의 아내 - 맹자자책 불감거부(孟子自責 不敢去婦)
- 맹자제사(서문) - 조기는 누구인가?
- 삼황오제(중국고대사) - 서경
- 제위왕과 순우곤 (사마천 골계열전)
- 조선은 맹자의 나라
- 보현tv
- 사랑하지 말자
- 사마천 사기열전
- 삼국통일과 한국통일
- 서양철학사 (YouTube)
- 1. 변화와 불변 - 끊임없는 형이상학과의 투쟁
- 28. 러셀의 기술이론1 Theory of Descriptions
- 45. 네오 플라토니즘 - 헬레니즘과 로마
- 52. 아우구스티누스 - 자유의지론
- 53. 성염의 아우구스티누스1 신앙과 이성 - 이해할려면 믿어라
- 54 성염의 아우구스티누스2 삼위일체론 - 성부 성자 성령은 '관계개념'
- 63. 박승찬교수의 토마스 아퀴나스 1 신앙과 이성의 조화
- 64 박승찬교수의 토마스 아퀴나스 2 신의 존재증명 - 아벨라르두스 'Sic et Non'
- 81. 바울이냐 예수냐 - 브레데 '메시아의 비밀'
- 82. 바울과 예수의 창조적 결합 - 바르트와 불트만
- 83. 기독교 이해의 단서 - 연속과 단절
- 스무살 반양심경에 미치다
- 시경(詩經)
- 우리는 누구인가(YouTube)
- 우린 너무 몰랐다. 해방, 제주 4.3, 여순민중항쟁
- 유시민과 도올 - 통일 청춘을 말하다
- 장자 - 그림으로 보는
- 절차탁마(切磋琢磨) 대기만성(大器晩成)
- 주역심리학 - 정신과 전문의 양창순
- 중용만화
- 중용의 맛
- 한국독립운동사 10부작 (YouTube)
- 한국인이 캐낸 그리스 문명 - 김승중
- Analects (논어)
Mathmatics in Ancient Greece
Mathmatics in Ancient Greece
Thales
- the first person to prove the truth of the theorem
- a theorem(정리, principle) is a statement or hypothesis that can be proved, based on accepted asioms(laws of mathmatics)
-
he determined the height of the Great Pyramid of Giza using its shadow
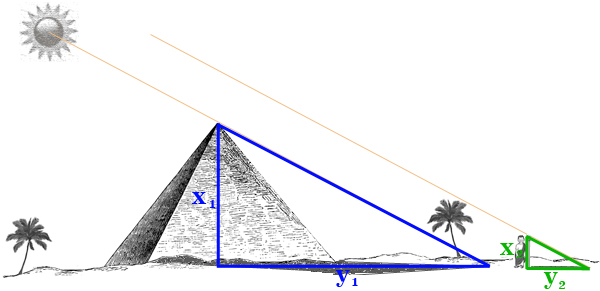
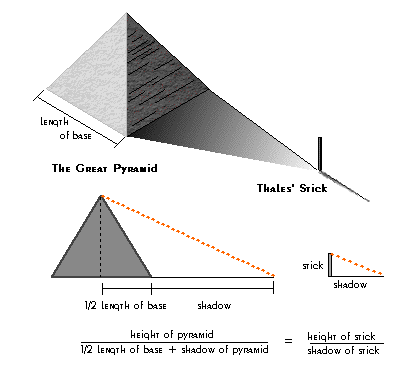
his famous theorem - the base angles of an isosceles triangle are equal
- when two straight lines interset, the opposing angles are equal
-
an angle in a semicircle is a right angle
- "geometry" comes from Greek word, geo, which means "earth", and metria meaning "measurement"
- Thales first created an abstract principle and axioms from examples by deductive reasoning
Pythagoras
- figurate numbers
- perfect numbers 1 + 2 + 3 = 6 is a perfect number
- pythagorean theorem was not actually discovered by Pythagoras. It was known to the Babylonians at least 1,000 years earlier
- Pythagoras was the first person to prove it.
- Euclid's Element proposition 47
The Pythagorean Theorem
Greek Mathmatics
Achilles and the Tortoise
-
Zeno if Ekea introduced the notion of infinity with his famouse paradoxes
Plato and his solid
- he believed that geometry held sacred truths describing the underlying nature of reality
-
when he founded a school called Academy in 387 BCE, the sign above the entrance said:
Let no one ignorant of geometry enter here

Eudoxos
- one of the most significant mathematicians to attend Plato's Academy
- he created a type of calculus used to find the area under a curve, developing the method of exhaustion
- he used his early form of calculus to prove that volume of the pyramid is one-third of prisms
-
also the volume of cone is one-third of cylinder
The method of exhaustion- The method of exhaustion (methodus exhaustionibus, or méthode des anciens) is a method of finding the area of a shape by inscribing inside it a sequence of polygons whose areas converge to the area of the containing shape.
The Three Classical Problems
- Squaring the circle means drawing a square with the same are as a given circle - pi came from this try.
- Doubling the cube means trying to construct a cube with precisely double the volume of another cube
-
Trisecting the angle means constructing an angle that is precisely one-third of a given angle
- all three of the classical problems have no solution
Euclid and His Elements
- he lived in Alexandria
- the father of geometry
- he compiled all kinds of geometry theorems
-
and wrote a book called, The Elements of Geometry, which became the most translated, published and studied book in the western world, second only to the Bible. the most famous textbook in history.
-
Khan Ademy Lecture
-
he started with basic assumptions, which are called axioms or postulates.
from them he proved a proposition, which is called theorem
no one has done this before - if you did not read this book you were not considered as intellect or educated
- What Euclid did was to really tighten our reasoning to prove something.
-
Arithmatic is just computation. Euclidean geometry is real mathmatics is about.
making some assumptions and then deducing other things from those assumptions
The Hellenistic period
-
The Hellenistic period covers the period of ancient Greek (Hellenic) history and Mediterranean history
between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire. - At this time, Greek cultural influence and power was at its peak in Europe, Africa and Asia
- The Hellenistic period saw the rise of New Comedy, Alexandrian poetry, the Septuagint and the philosophies of Stoicism and Epicureanism.
- Greek Science was advanced by the works of the mathematician Euclid and the polymath Archimedes.
Archimedes
-
he came up with the idea, not in a bath tub, but in an attempt to build a huge ship, Syracusia
-
ancient Greek ship sometimes claimed to be the largest transport ship of antiquity.
She only sailed once, from Syracuse in Sicily to Alexandria in the Ptolemaic Kingdom.


-
Law of Buoyancy or Archimedes' Principlebasically you need as much water as the weight of floating object
-
he also invented Archimedes Screw

a machine historically used for transferring water from a low-lying body of water into irrigation ditches. Water is pumped by turning a screw-shaped surface inside a pipe.
Eratosthenes
- a contemporary of Archimedes
-
he measured the circumference of the earth
-
when he calculate this, he used two propositions from Euclid
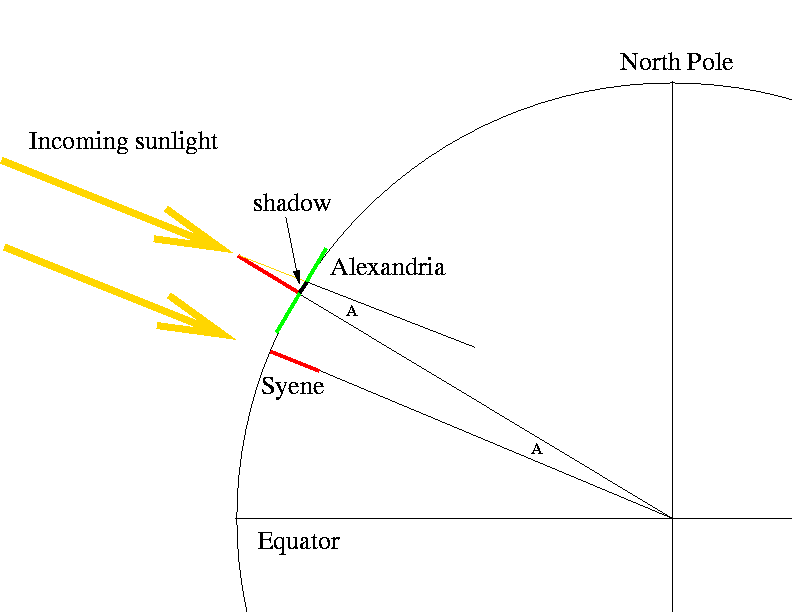
- 1. eratosthenes.gif7K2016-09-10
- 2. syracusia2.jpg800K2016-09-12
- 3. syracusia.png432K2016-09-12
- 4. PythagoreanTheorem.gif6K2019-07-02
- 5. pythagorean-theorem-proof.jpg79K2019-07-02
jdoc/comment/add
jdoc/comment/delete